NanoCAD, a powerful and versatile CAD software, stands at the forefront of 2D and 3D design solutions. Its intuitive interface and comprehensive features make it an ideal choice for professionals and hobbyists alike, offering a robust platform for creating intricate designs, drafting blueprints, and visualizing complex structures.
Table of Contents
Developed with an emphasis on user-friendliness and efficiency, NanoCAD empowers users to navigate the design process with ease. From basic drafting tools to advanced modeling capabilities, the software provides a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline workflows and enhance productivity. Whether you’re an architect sketching a building plan, an engineer designing intricate machinery, or a hobbyist creating a 3D model, NanoCAD offers the tools and flexibility to bring your visions to life.
NanoCAD Applications
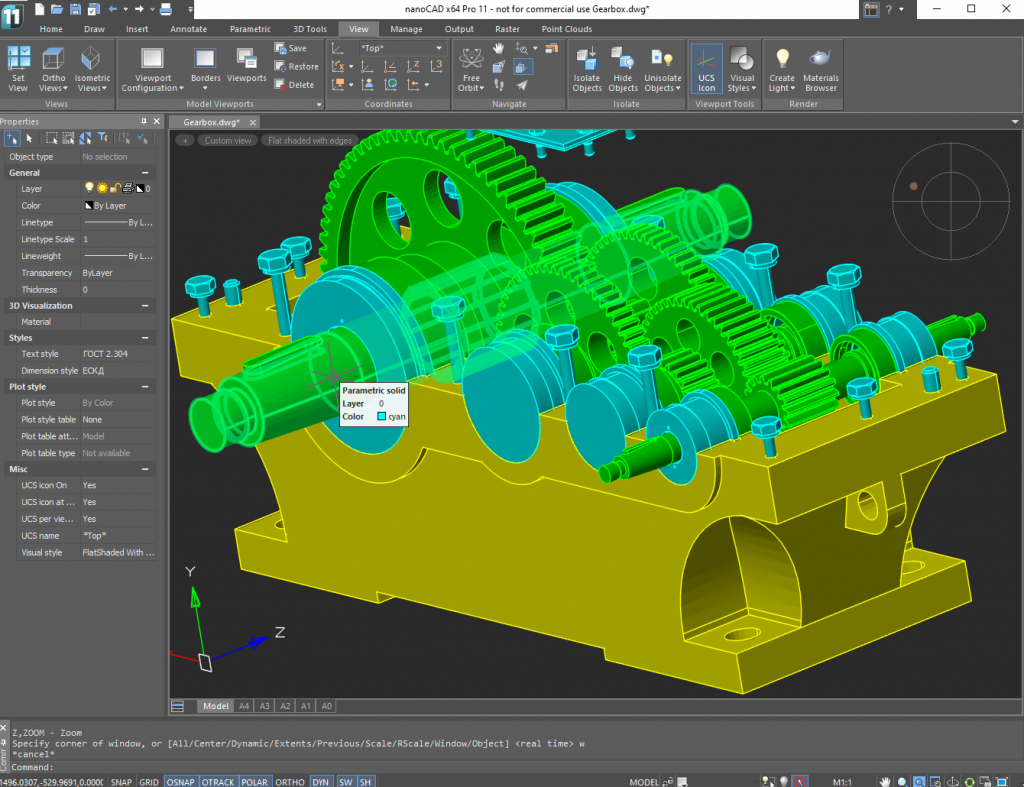
NanoCAD is a versatile CAD software with a wide range of applications across various industries. It offers a cost-effective solution for 2D and 3D design, making it suitable for professionals and individuals alike.
Engineering
NanoCAD is extensively used in various engineering disciplines, including mechanical, civil, and electrical engineering. It facilitates the creation of detailed drawings, schematics, and models for diverse engineering projects.
- Mechanical Engineering: NanoCAD enables the design and analysis of mechanical components, assemblies, and systems. It supports features like parametric modeling, drafting, and simulation, facilitating the creation of precise and efficient designs.
- Civil Engineering: NanoCAD is utilized for designing infrastructure projects, including buildings, bridges, and roads. Its capabilities in creating 2D and 3D models, along with its integration with other software, make it a valuable tool for civil engineers.
- Electrical Engineering: NanoCAD aids in the design and documentation of electrical systems, including wiring diagrams, circuit layouts, and panel designs. Its features, such as electrical symbols and schematic creation tools, enhance efficiency in electrical engineering projects.
Architecture
NanoCAD plays a crucial role in architectural design and planning. It empowers architects to create detailed floor plans, elevations, sections, and 3D models, facilitating the visualization and communication of design ideas.
- Building Design: NanoCAD assists in the creation of architectural drawings for residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Its features for creating walls, doors, windows, and other architectural elements streamline the design process.
- Interior Design: NanoCAD enables architects and interior designers to visualize and plan interior spaces. It supports the creation of furniture layouts, lighting plans, and other interior design elements, enhancing the design process.
- Landscape Design: NanoCAD can be used for landscape design, allowing for the creation of plans for gardens, parks, and other outdoor spaces. It supports the inclusion of trees, plants, and other landscaping features, facilitating the visualization of outdoor spaces.
Design
NanoCAD is used by designers in various fields, including product design, graphic design, and industrial design. It offers tools for creating 2D and 3D models, allowing designers to visualize and refine their designs.
- Product Design: NanoCAD supports the creation of detailed product designs, including 3D models, technical drawings, and assembly instructions. It enables designers to create prototypes and test different design concepts, facilitating the development of innovative products.
- Graphic Design: NanoCAD can be used for creating logos, illustrations, and other graphic design elements. Its vector-based drawing capabilities and integration with other design software make it a valuable tool for graphic designers.
- Industrial Design: NanoCAD assists industrial designers in creating models and drawings for industrial products, such as furniture, appliances, and machinery. Its features for creating complex 3D models and technical drawings enhance the design and manufacturing process.
NanoCAD Features
NanoCAD is a popular CAD software known for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive set of tools. Its features cater to both beginners and experienced users, making it suitable for various design and drafting tasks.
User Interface and Navigation
NanoCAD boasts a user-friendly interface designed to simplify the design process. It offers a familiar layout with toolbars, menus, and a command line interface. The ribbon interface provides easy access to frequently used tools, while the command line interface allows for precise control and customization. Users can navigate through the interface using the mouse, keyboard shortcuts, or a combination of both. The intuitive design allows for quick learning and efficient workflow.
Drawing and Editing Tools
NanoCAD provides a wide range of drawing and editing tools to create and modify 2D and 3D designs. The software includes tools for:
- Line, Arc, Circle, and Polyline Creation: These tools allow users to create basic geometric shapes with various options for customization, such as line thickness, color, and style.
- Dimensioning: NanoCAD offers comprehensive dimensioning tools for adding accurate measurements to drawings. Users can create linear, angular, radial, and diameter dimensions, among others.
- Text and Annotation: The software allows users to add text and annotations to drawings for clarity and communication. Users can customize text font, size, style, and alignment.
- Object Modification: NanoCAD provides tools for modifying existing objects, such as moving, copying, rotating, scaling, and mirroring. These tools enable users to easily adjust and refine their designs.
- Layers and Groups: The software supports layers and groups for organizing and managing complex drawings. Users can create multiple layers and assign different properties to each layer, such as color, line style, and visibility. Groups allow users to combine multiple objects into a single entity for easier manipulation.
- Snapping and Constraints: NanoCAD includes snapping and constraint tools for creating accurate and consistent designs. Snapping tools help users precisely align objects to existing geometry, while constraints ensure that objects maintain specific relationships, such as parallel, perpendicular, or tangent.
- Block Creation and Insertion: Users can create and insert custom blocks, which are reusable components, to simplify the design process and maintain consistency. Blocks can be created from existing geometry or imported from external files.
2D and 3D Modeling Capabilities
NanoCAD is a versatile software capable of creating both 2D and 3D models.
2D Modeling
NanoCAD provides a robust set of tools for creating detailed 2D drawings. Users can create floor plans, elevations, sections, and other architectural, mechanical, and electrical drawings. The software supports various drafting standards, including ISO, ANSI, and DIN.
3D Modeling
While NanoCAD is primarily known for its 2D capabilities, it also offers tools for basic 3D modeling. Users can create 3D objects using extrusion, revolution, and other techniques. The software supports various 3D modeling tools, including:
- Extrude: This tool creates 3D objects by extending a 2D shape along a specified direction.
- Revolve: This tool creates 3D objects by rotating a 2D shape around a specified axis.
- Sweep: This tool creates 3D objects by sweeping a 2D shape along a specified path.
- Loft: This tool creates 3D objects by connecting two or more cross-sections.
NanoCAD also supports rendering and visualization tools for creating realistic representations of 3D models.
NanoCAD Compatibility and Integration
NanoCAD’s compatibility with other software and file formats is a key factor in its versatility and ease of use. This section explores NanoCAD’s compatibility with other design and engineering workflows and its limitations.
File Format Compatibility, Nanocad
NanoCAD supports a wide range of file formats, making it possible to work with files created in other CAD software. This ensures a smooth workflow and seamless integration with other design and engineering tools.
- Native Formats: NanoCAD uses its own native DWG format, which is compatible with all versions of AutoCAD. This allows for easy sharing and collaboration with users of other CAD software.
- Industry Standard Formats: NanoCAD also supports various industry-standard formats, including DXF, DWF, and PDF. This ensures compatibility with a wide range of software and applications.
- Other Formats: In addition to these common formats, NanoCAD also supports formats like STL, IGES, and STEP, which are used in 3D modeling and manufacturing.
Software Integration
NanoCAD can be integrated with various software applications, enhancing its capabilities and expanding its functionality. This integration allows users to leverage the strengths of other software while working within NanoCAD.
- BIM Software: NanoCAD can be integrated with BIM software, such as Revit, to exchange data and collaborate on projects. This allows for seamless coordination between architectural and engineering disciplines.
- FEA Software: Integration with FEA software, like ANSYS or Abaqus, enables users to perform structural analysis on NanoCAD designs. This allows for the evaluation of design performance and optimization.
- CAM Software: Integration with CAM software, such as Mastercam or Fusion 360, enables users to generate toolpaths for CNC machining directly from NanoCAD designs. This streamlines the manufacturing process and reduces errors.
Limitations
While NanoCAD offers a high degree of compatibility and integration, it does have some limitations:
- Limited Support for Specialized Formats: NanoCAD may not support all specialized formats used in specific industries, such as those used in aerospace or automotive design. This can limit the ability to work with certain files.
- Compatibility Issues with Older Versions: Compatibility issues can arise when working with files created in older versions of AutoCAD or other CAD software. This can require file conversion or adjustments to ensure proper functionality.
- Limited Integration with Specific Software: NanoCAD’s integration capabilities may not extend to all software applications. Users may need to rely on third-party plugins or workarounds to achieve full integration.
NanoCAD Tutorials and Resources
NanoCAD provides a comprehensive range of tutorials and resources to help users learn and master the software. These resources cater to various learning styles and skill levels, ensuring that users can find the information they need to effectively utilize NanoCAD.
Available Tutorials and Resources
These resources offer a variety of learning materials, including official documentation, online forums, and video tutorials.
- Official NanoCAD Documentation: The official NanoCAD documentation is a comprehensive resource that covers all aspects of the software, from basic concepts to advanced features. This documentation is available in both online and offline formats, making it accessible to users regardless of their internet connection.
- NanoCAD Online Forums: Online forums are a great place to connect with other NanoCAD users, ask questions, and share tips and tricks. These forums are moderated by experienced NanoCAD users who can provide helpful advice and support.
- NanoCAD Video Tutorials: Video tutorials provide a visual and interactive way to learn NanoCAD. These tutorials cover a wide range of topics, from basic commands to complex workflows. They are available on various platforms, such as YouTube and the NanoCAD website.
NanoCAD Tutorials and Resources
This table lists various resources, their descriptions, and their levels of difficulty.
| Resource | Description | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|
| Official NanoCAD Documentation | Comprehensive resource covering all aspects of the software | Beginner to Advanced |
| NanoCAD Online Forums | Platform for connecting with other users, asking questions, and sharing tips | Beginner to Advanced |
| NanoCAD Video Tutorials | Visual and interactive learning materials covering various topics | Beginner to Advanced |
| NanoCAD Training Courses | Structured learning programs offered by authorized training providers | Beginner to Advanced |
NanoCAD Case Studies
NanoCAD has been successfully implemented in a wide range of projects across various industries. These case studies demonstrate the software’s capabilities and provide valuable insights into its real-world applications.
Examples of Successful NanoCAD Implementations
This section showcases real-world examples of how NanoCAD has been used to solve engineering challenges and achieve project goals. Each case study highlights the specific benefits and outcomes realized by using NanoCAD.
- Project: Design and Construction of a New Shopping Mall
- Industry: Architecture and Construction
- Challenge: Creating detailed 2D and 3D drawings for the mall’s structural elements, including floors, walls, and roof, while adhering to strict building codes and regulations.
- Solution: NanoCAD’s powerful drawing tools and compatibility with industry-standard file formats enabled the architects to create accurate and comprehensive plans, elevations, and sections. The software’s ability to handle complex geometry and generate precise drawings ensured compliance with building codes and facilitated smooth construction.
- Outcomes: The project was completed on time and within budget, with minimal revisions and rework. The use of NanoCAD facilitated efficient communication between the design team and contractors, leading to a seamless construction process.
- Lessons Learned: NanoCAD’s user-friendly interface and comprehensive features made it easy for the design team to learn and adopt the software quickly. The software’s affordability compared to other CAD solutions allowed the firm to allocate resources effectively and achieve cost savings.
Challenges Faced and Solutions Achieved
This section delves into specific challenges encountered in NanoCAD projects and the solutions implemented to overcome them.
- Challenge: Integrating NanoCAD with existing BIM workflows and data management systems.
- Solution: NanoCAD’s compatibility with industry-standard file formats, such as DWG and IFC, allows for seamless integration with other BIM software. This ensures data consistency and facilitates collaboration between different project stakeholders.
- Challenge: Training and onboarding new users to effectively utilize NanoCAD’s features.
- Solution: NanoCAD offers comprehensive documentation, online tutorials, and training courses to assist users in mastering the software’s functionalities. The company also provides dedicated support services to address user queries and technical issues.
Case Study Table
This table summarizes key information from various NanoCAD projects, highlighting project details, outcomes, and lessons learned.
| Project | Industry | Challenge | Solution | Outcomes | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Design and Construction of a New Shopping Mall | Architecture and Construction | Creating detailed 2D and 3D drawings for the mall’s structural elements, including floors, walls, and roof, while adhering to strict building codes and regulations. | NanoCAD’s powerful drawing tools and compatibility with industry-standard file formats enabled the architects to create accurate and comprehensive plans, elevations, and sections. The software’s ability to handle complex geometry and generate precise drawings ensured compliance with building codes and facilitated smooth construction. | The project was completed on time and within budget, with minimal revisions and rework. The use of NanoCAD facilitated efficient communication between the design team and contractors, leading to a seamless construction process. | NanoCAD’s user-friendly interface and comprehensive features made it easy for the design team to learn and adopt the software quickly. The software’s affordability compared to other CAD solutions allowed the firm to allocate resources effectively and achieve cost savings. |
| Mechanical Design of a New Automotive Engine | Automotive Engineering | Creating complex 3D models of engine components, including pistons, connecting rods, and crankshaft, while ensuring dimensional accuracy and tolerance control. | NanoCAD’s advanced 3D modeling tools and parametric design capabilities allowed the engineers to create precise and detailed models of engine components. The software’s support for various engineering units and tolerances ensured compliance with industry standards. | The engine design process was accelerated, leading to faster prototyping and testing. The use of NanoCAD enabled the engineers to identify and resolve design flaws early in the development cycle, reducing potential manufacturing issues. | NanoCAD’s powerful 3D modeling features and parametric design capabilities significantly enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of the design process. The software’s ability to handle complex geometries and perform advanced analysis enabled the engineers to create a robust and reliable engine design. |
| Electrical Design of a High-Rise Building | Electrical Engineering | Developing detailed electrical plans, including wiring diagrams, circuit layouts, and equipment specifications, while adhering to safety codes and industry standards. | NanoCAD’s electrical design tools and libraries of symbols and components facilitated the creation of accurate and comprehensive electrical plans. The software’s ability to perform electrical calculations and generate reports ensured compliance with safety codes and regulations. | The electrical design process was streamlined, reducing errors and ensuring compliance with industry standards. The use of NanoCAD facilitated efficient communication between the electrical engineers and contractors, leading to a smooth installation process. | NanoCAD’s specialized electrical design features and comprehensive library of symbols and components simplified the design process and ensured accuracy. The software’s ability to generate reports and documentation facilitated project management and communication. |
Future of NanoCAD
NanoCAD, as a robust and versatile CAD software, is poised for continued growth and evolution. Its future hinges on adapting to emerging trends in the CAD industry, embracing innovative technologies, and catering to the evolving needs of its user base.
Emerging Trends in CAD Software
The CAD software landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, user expectations, and industry demands. Several key trends are shaping the future of CAD, which NanoCAD will need to adapt to remain competitive:
- Cloud-based CAD: Cloud computing is transforming the way CAD software is accessed and used. Cloud-based CAD solutions offer several advantages, including increased accessibility, collaboration, and data storage. NanoCAD could leverage cloud technology to enhance its platform, allowing users to work from anywhere and collaborate seamlessly with others.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is revolutionizing various industries, and CAD is no exception. AI-powered features can automate tasks, improve design accuracy, and provide intelligent insights. NanoCAD could integrate AI capabilities to streamline design workflows, enhance design quality, and provide predictive analytics.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR technologies are gaining traction in the design and engineering fields, providing immersive experiences and enhanced visualization. NanoCAD could integrate VR/AR capabilities to enable users to interact with their designs in a more realistic and engaging way.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of connected devices is driving the need for CAD software that can handle complex IoT projects. NanoCAD could adapt to this trend by incorporating features that support IoT design, simulation, and analysis.
Potential New Features and Integrations
NanoCAD has the potential to introduce new features and integrations that enhance its functionality and cater to the needs of its users:
- Advanced Parametric Modeling: NanoCAD could incorporate advanced parametric modeling capabilities, allowing users to create and modify designs based on parameters and constraints. This would streamline the design process and enable greater design flexibility.
- Enhanced Collaboration Tools: NanoCAD could introduce advanced collaboration tools, allowing users to work together on projects seamlessly. This could include real-time collaboration features, version control, and integrated communication tools.
- Integration with BIM Software: NanoCAD could integrate with Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, enabling users to seamlessly transfer design data between CAD and BIM platforms. This would streamline the design and construction process and facilitate greater interoperability.
- Advanced Rendering Capabilities: NanoCAD could enhance its rendering capabilities, providing users with more realistic and detailed visualizations. This would improve the communication of design intent and enable more effective presentations.
- Customization and App Store: NanoCAD could develop an app store or marketplace where users can access and download custom tools, plugins, and extensions. This would allow users to tailor NanoCAD to their specific needs and workflows.
Closure
NanoCAD’s intuitive interface, robust features, and affordability make it a compelling choice for individuals and businesses seeking a powerful yet accessible CAD solution. As technology continues to evolve, NanoCAD is poised to remain a leading force in the world of 2D and 3D design, empowering users to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
NanoCAD is a powerful 2D and 3D CAD software that’s perfect for creating detailed drawings and designs. Once you’ve completed your work in NanoCAD, you might need to share it with others in a universally accessible format like PDF. For that, you can easily download a PDF creator like the one available at pdf creator download.
This allows you to convert your NanoCAD designs into PDFs, ensuring that they can be viewed and shared without any compatibility issues.
