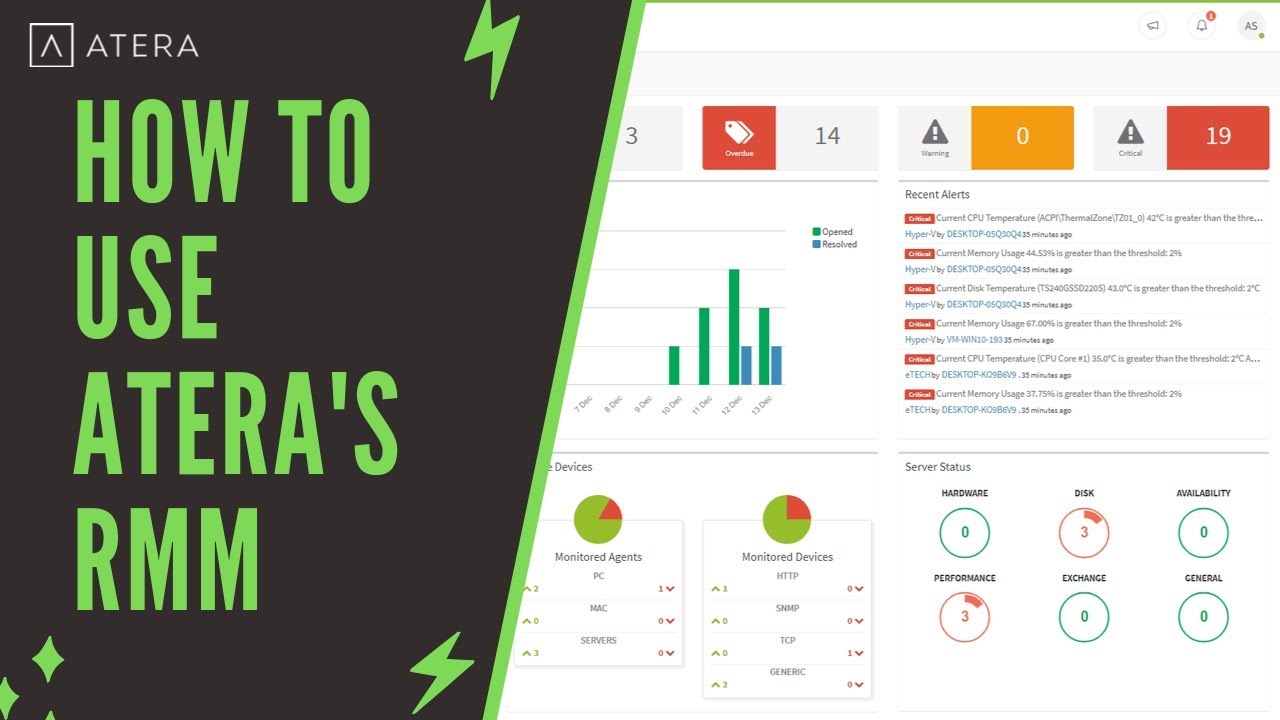
All in one rmm – All-in-One RMM, a powerful tool for IT professionals, provides a centralized platform to manage and monitor your entire IT infrastructure. This approach consolidates numerous essential functionalities, offering a streamlined and comprehensive solution for managing endpoints, security, backups, and more.
Table of Contents
Imagine having a single dashboard to oversee all your IT operations, from patching vulnerabilities to monitoring system health and responding to user requests. All-in-One RMM makes this vision a reality, eliminating the need for multiple disparate tools and simplifying IT management.
What is an RMM?
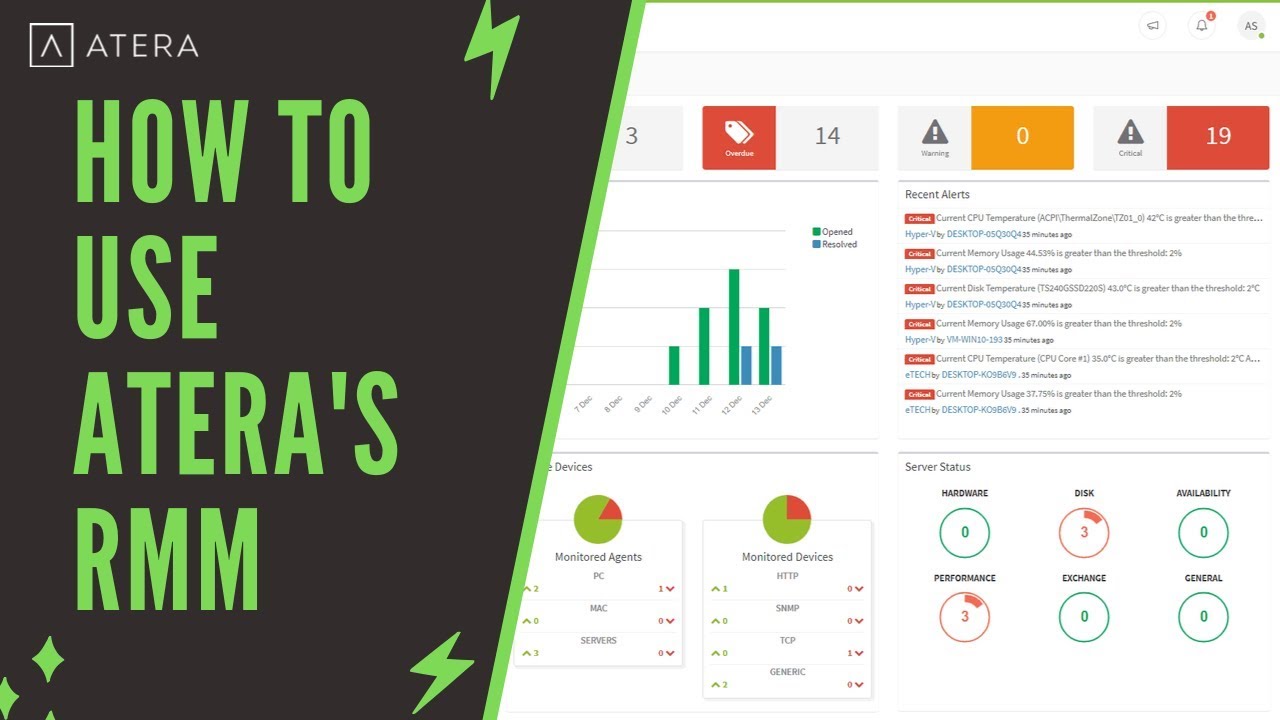
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) is a powerful tool that allows businesses to manage and monitor their IT infrastructure remotely. Think of it as a central hub for all your IT needs, giving you complete control over your systems and devices from anywhere in the world.
Core Functionalities
An RMM solution offers a wide range of functionalities that streamline IT management and enhance security.
- Remote Monitoring: RMM systems continuously monitor your devices for performance issues, security threats, and software updates, alerting you to potential problems before they escalate.
- Remote Control: You can remotely access and control your devices, allowing you to troubleshoot problems, install software, and manage configurations, all without physically being present.
- Patch Management: RMM solutions automate the process of installing software updates and security patches, ensuring your systems are protected from vulnerabilities.
- Asset Management: RMM tools provide a comprehensive inventory of your IT assets, including hardware, software, and licenses, making it easier to track and manage your resources.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM systems generate insightful reports on system performance, security threats, and user activity, providing valuable data for informed decision-making.
Benefits of Implementing an RMM System
Implementing an RMM system can bring numerous benefits to businesses of all sizes.
- Improved Security: By automating patch management and providing real-time monitoring, RMM solutions strengthen your cybersecurity posture and minimize the risk of breaches.
- Enhanced Productivity: Proactive monitoring and remote access allow IT teams to resolve issues quickly, minimizing downtime and maximizing employee productivity.
- Reduced Costs: RMM solutions can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives and reducing the need for expensive on-site support.
- Increased Scalability: RMM systems can easily adapt to growing businesses, providing a scalable solution for managing expanding IT infrastructure.
- Improved Compliance: RMM tools can help organizations meet compliance requirements by automating tasks and providing documentation for audits.
Essential Features of an All-in-One RMM: All In One Rmm
An all-in-one RMM solution offers a comprehensive suite of tools that simplify IT management, enhance security, and optimize performance. By integrating various functionalities, these platforms streamline operations and provide a unified view of your IT infrastructure.
Endpoint Management
Endpoint management is a critical aspect of any IT infrastructure, as it involves controlling and managing all devices connected to your network. This feature enables you to:
- Inventory and Configuration Management: Track all devices, software, and hardware assets, providing a clear picture of your IT environment. This facilitates efficient resource allocation, software licensing, and security audits.
- Software Deployment and Updates: Deploy software updates and patches automatically, ensuring all devices are running the latest versions and minimizing vulnerabilities.
- Remote Control and Management: Access and control endpoints remotely, troubleshoot issues, and perform tasks without physically being present. This saves time and resources, especially for geographically dispersed teams.
- Security Policies and Enforcement: Define and enforce security policies, such as password complexity requirements, antivirus updates, and firewall settings, to protect your network from unauthorized access and threats.
Patch Management
Patch management is crucial for mitigating security risks by ensuring all devices are updated with the latest security patches. This feature:
- Automated Patch Scanning and Deployment: Automatically scan for missing patches and deploy them to all devices, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities exploited by attackers.
- Patch Approval and Scheduling: Control the patch deployment process by approving patches before they are applied, scheduling deployments during off-peak hours to minimize disruptions.
- Patch Reporting and Analytics: Monitor patch compliance and identify devices that haven’t been patched, enabling proactive security management.
Security Monitoring
Security monitoring is vital for detecting and responding to potential threats, including malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches. This feature:
- Real-time Threat Detection: Continuously monitor endpoints for suspicious activity, such as unusual file access, network connections, and process behavior.
- Security Event Logging and Analysis: Record security events and analyze them to identify patterns and potential threats. This helps in investigating incidents and improving security posture.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Protection: Protect endpoints from known and emerging threats with integrated antivirus and anti-malware software, providing a comprehensive defense against malicious attacks.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Detect and block unauthorized access attempts and malicious activity, preventing attackers from gaining access to sensitive data.
Backup and Recovery
Data backup and recovery are essential for business continuity, enabling you to restore data in case of system failures, disasters, or ransomware attacks. This feature:
- Automated Data Backup: Schedule regular backups of critical data, ensuring data integrity and availability in case of unexpected events.
- Data Encryption and Security: Encrypt backups to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: Define and implement disaster recovery plans, outlining procedures for restoring systems and data after an incident, minimizing downtime and data loss.
- Versioning and Retention Policies: Store multiple versions of backups, enabling you to restore data to a specific point in time, and define retention policies to manage storage space effectively.
Reporting and Analytics, All in one rmm
Reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into your IT infrastructure, helping you make informed decisions and optimize performance. This feature:
- Customizable Reports and Dashboards: Generate reports and dashboards tailored to your specific needs, providing a clear overview of key metrics, such as device health, security posture, and user activity.
- Trend Analysis and Forecasting: Analyze historical data to identify trends and patterns, allowing you to anticipate future needs and proactively address potential issues.
- Performance Monitoring and Optimization: Monitor system performance and identify bottlenecks, enabling you to optimize resource allocation and improve overall efficiency.
- Compliance Reporting: Generate reports that demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and security standards, ensuring your organization meets legal and ethical requirements.
Help Desk and Ticketing
Help desk and ticketing systems streamline IT support by providing a centralized platform for managing requests, incidents, and issues. This feature:
- Ticket Submission and Tracking: Users can submit support requests through a web portal or email, and IT staff can track the progress of each ticket, ensuring timely resolution.
- Knowledge Base and Self-Service: Provide users with access to a knowledge base of common solutions and troubleshooting guides, enabling them to resolve issues independently and reduce support workload.
- SLA Management: Define service level agreements (SLAs) for different types of support requests, ensuring that users receive timely and effective assistance.
- Reporting and Analytics: Track key metrics, such as ticket volume, resolution time, and customer satisfaction, providing insights into support performance and identifying areas for improvement.
Asset Management
Asset management is essential for tracking and managing all hardware and software assets within your IT infrastructure. This feature:
- Inventory and Tracking: Maintain a comprehensive inventory of all assets, including details such as serial numbers, purchase dates, and warranty information.
- Lifecycle Management: Track the lifecycle of each asset, from acquisition to disposal, ensuring compliance with regulations and optimizing asset utilization.
- Software Licensing Management: Manage software licenses, ensuring compliance with vendor agreements and preventing unauthorized use.
- Auditing and Reporting: Generate reports on asset utilization, license compliance, and other key metrics, providing valuable insights for decision-making.
Remote Control
Remote control capabilities allow IT staff to access and control endpoints remotely, enabling them to troubleshoot issues, perform tasks, and provide support without physically being present. This feature:
- Remote Desktop Access: Access the desktop of any endpoint remotely, enabling you to view the screen, interact with applications, and troubleshoot issues.
- File Transfer and Management: Transfer files between endpoints and the central management console, facilitating data sharing and remote troubleshooting.
- Remote Command Execution: Execute commands and scripts on remote endpoints, automating tasks and streamlining operations.
- Security and Access Control: Implement robust security measures, such as multi-factor authentication and encryption, to protect remote access sessions.
Final Summary
In a world where technology constantly evolves, embracing an all-in-one RMM solution is a strategic move for businesses of all sizes. It fosters a proactive approach to IT management, empowering organizations to enhance security, boost efficiency, and optimize their IT investments. By simplifying complex tasks and providing a unified platform, all-in-one RMM empowers businesses to focus on their core operations while ensuring a robust and reliable IT environment.
An all-in-one RMM solution can streamline your IT operations, offering features like remote monitoring, patch management, and endpoint security. For more complex tasks, like 3D model creation from images, you might consider tools like metashape. While not directly related to RMM, such tools can enhance your ability to manage and visualize assets, further improving your overall IT infrastructure management.