RMM monitoring software sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. RMM, or Remote Monitoring and Management, software empowers IT professionals to oversee and manage computer systems remotely, enabling efficient troubleshooting, proactive maintenance, and enhanced security. This powerful technology is a game-changer for businesses of all sizes, streamlining IT operations and ensuring seamless productivity.
Table of Contents
RMM monitoring software provides a comprehensive suite of tools that encompass remote access, patch management, endpoint security, and detailed reporting. By leveraging these features, IT teams can proactively identify and resolve issues before they escalate, minimizing downtime and maximizing uptime. Additionally, RMM software empowers businesses to implement robust security measures, safeguarding sensitive data and protecting against cyber threats. This technology has revolutionized IT management, offering a centralized platform for monitoring, managing, and securing networks and devices, ensuring efficient operations and peace of mind.
Benefits of Using RMM Monitoring Software
RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) software offers a wide range of advantages for businesses of all sizes, particularly in today’s digital landscape where technology plays a crucial role in daily operations. From streamlining IT tasks to enhancing security and boosting productivity, RMM software empowers businesses to optimize their IT infrastructure and achieve greater efficiency.
Reduced IT Costs
RMM software significantly contributes to cost reduction by automating routine IT tasks and minimizing the need for on-site visits. By automating tasks such as software updates, patch management, and system backups, RMM software frees up valuable IT staff time, allowing them to focus on more complex and strategic initiatives.
- Automated Patch Management: RMM software automates the process of identifying and installing software updates and security patches, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and ensuring that systems are protected from potential threats. This automated approach eliminates the manual effort required for patch management, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
- Remote System Monitoring: RMM software enables IT professionals to remotely monitor the performance and health of devices, servers, and networks, providing real-time insights into potential issues. This proactive approach allows IT staff to address problems before they escalate into major disruptions, minimizing downtime and reducing the need for costly on-site interventions.
- Reduced On-site Visits: By enabling remote access and control, RMM software minimizes the need for on-site visits, saving businesses time and money. This is particularly beneficial for organizations with geographically dispersed locations or limited IT staff, as it allows them to manage their IT infrastructure efficiently without the need for extensive travel.
Enhanced Security
RMM software plays a critical role in strengthening IT security by providing comprehensive monitoring and control capabilities. The ability to remotely monitor and manage devices, enforce security policies, and detect suspicious activity enables businesses to proactively identify and address potential security threats.
- Real-time Threat Detection: RMM software continuously monitors systems for suspicious activity, providing alerts for potential security breaches. This real-time monitoring enables businesses to quickly identify and respond to threats, minimizing the impact of security incidents.
- Vulnerability Scanning: RMM software performs regular vulnerability scans to identify weaknesses in systems and applications. This proactive approach allows businesses to address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers, reducing the risk of security breaches.
- Endpoint Security Management: RMM software enables businesses to enforce security policies across all endpoints, including laptops, desktops, and mobile devices. This centralized approach ensures that all devices are protected by the same security measures, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Improved Productivity
RMM software streamlines IT processes and enhances productivity by automating routine tasks, providing real-time insights, and minimizing downtime. By freeing up IT staff time and reducing disruptions, RMM software empowers businesses to focus on strategic initiatives and achieve greater efficiency.
- Automated Task Management: RMM software automates repetitive tasks such as software updates, patch management, and system backups, allowing IT staff to focus on more complex and strategic projects. This automated approach reduces the time spent on mundane tasks, freeing up IT staff to work on initiatives that drive business growth.
- Real-time Performance Monitoring: RMM software provides real-time insights into system performance, allowing IT staff to proactively identify and address potential issues before they impact productivity. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures that systems are running smoothly, maximizing user productivity.
- Centralized Management: RMM software centralizes the management of IT infrastructure, providing a single platform for monitoring, controlling, and managing devices, applications, and networks. This centralized approach simplifies IT operations and enhances efficiency, reducing the time and effort required to manage IT infrastructure.
Increased Uptime
RMM software plays a vital role in maximizing uptime by proactively monitoring systems, detecting potential issues, and enabling swift remediation. By identifying and addressing problems before they escalate into major disruptions, RMM software ensures that businesses can continue operating smoothly, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
- Proactive Monitoring: RMM software continuously monitors systems for potential issues, providing alerts for performance degradation, hardware failures, and other problems. This proactive approach enables IT staff to address issues before they impact business operations, minimizing downtime and ensuring system stability.
- Remote Access and Control: RMM software provides remote access and control capabilities, allowing IT staff to quickly diagnose and resolve issues without the need for on-site visits. This remote access enables swift remediation, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
- Automated System Recovery: RMM software can automate system recovery processes, such as restoring backups or reinstalling operating systems, in the event of a failure. This automated approach reduces the time and effort required to recover from system failures, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Implementing RMM Monitoring Software
Implementing RMM monitoring software can significantly improve your IT infrastructure management, but it requires careful planning and execution. This section delves into the key steps involved in successfully integrating RMM software into your existing IT environment.
Planning
Planning is crucial for a smooth and successful RMM implementation. It involves understanding your specific needs, defining objectives, and choosing the right RMM software.
- Define your goals: Clearly define what you hope to achieve with RMM. Are you aiming to improve endpoint security, automate tasks, reduce help desk tickets, or gain better visibility into your IT infrastructure? Understanding your goals will guide your selection of features and functionalities.
- Assess your current IT infrastructure: Analyze your existing network infrastructure, devices, operating systems, and applications. This will help you determine the complexity of the implementation and identify any potential compatibility issues.
- Evaluate RMM software options: Research and compare different RMM software solutions based on features, pricing, compatibility, and user reviews. Consider factors such as the size of your organization, the complexity of your IT environment, and your budget.
- Develop an implementation plan: Create a detailed plan outlining the steps involved, timelines, and resources required. This plan should include roles and responsibilities, communication strategies, and potential contingencies.
Installation
The installation process involves deploying the RMM agent on each device you want to monitor. This agent collects data and communicates with the RMM server.
- Choose the right deployment method: Select the most suitable method for deploying the RMM agent, such as manual installation, automated deployment, or group policy deployment. The choice depends on your IT infrastructure and security policies.
- Ensure compatibility: Verify that the RMM agent is compatible with the operating systems and devices in your environment. Check for any specific requirements or limitations.
- Configure network settings: Configure the RMM agent to communicate with the RMM server through your firewall and network settings. This may involve creating exceptions or adjusting security policies.
- Test the installation: After deploying the agents, test the installation to ensure they are communicating with the RMM server and collecting data correctly. This will help identify and resolve any issues early on.
Configuration
Once the RMM agents are installed, you need to configure the software to meet your specific requirements. This involves setting up monitoring policies, defining alerts, and customizing reports.
- Establish monitoring policies: Define what you want to monitor, such as CPU usage, disk space, security vulnerabilities, or software updates. Configure the RMM software to collect and analyze data according to your needs.
- Set up alerts and notifications: Configure alerts for critical events, such as system failures, security breaches, or high resource utilization. Define notification methods, such as email, SMS, or in-app notifications.
- Customize reporting: Configure the RMM software to generate reports that provide valuable insights into your IT infrastructure. This could include reports on system performance, security status, or software inventory.
- Integrate with existing tools: Consider integrating the RMM software with other IT tools, such as ticketing systems, security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, or asset management systems. This can streamline your workflows and improve data sharing.
Training
Training is essential to ensure that your IT team can effectively use the RMM software. This involves providing hands-on training on features, functionalities, and troubleshooting techniques.
- Develop a training plan: Create a comprehensive training plan that covers all aspects of the RMM software, from basic usage to advanced features. Include practical exercises and real-world scenarios.
- Provide access to resources: Offer access to documentation, tutorials, and online forums to support ongoing learning and troubleshooting. Encourage users to explore the software and experiment with different features.
- Offer ongoing support: Provide ongoing support to your IT team through dedicated support channels, regular meetings, or webinars. Address any questions or concerns promptly and effectively.
Best Practices for Integration, Rmm monitoring software
Integrating RMM software with your existing IT infrastructure requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some best practices to ensure a smooth and effective integration:
- Start small and scale gradually: Begin by implementing RMM on a small group of devices and gradually expand to your entire IT infrastructure. This allows you to test the software and identify any potential issues before deploying it widely.
- Prioritize security: Ensure that the RMM software meets your security standards and complies with relevant regulations. Implement strong authentication measures and monitor access permissions.
- Automate tasks: Leverage the automation capabilities of RMM to streamline routine tasks, such as software updates, patch management, and script execution. This can free up your IT team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Monitor performance and adjust settings: Regularly monitor the performance of the RMM software and adjust settings as needed. This ensures optimal performance and avoids any bottlenecks or issues.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementing RMM monitoring software can present some challenges, but with proper planning and execution, you can overcome them. Here are some common challenges and solutions:
- Resistance to change: Some IT staff may resist adopting new software or processes. Address this by emphasizing the benefits of RMM and providing adequate training and support.
- Compatibility issues: Ensure the RMM software is compatible with your existing operating systems, devices, and applications. Test the software thoroughly before deploying it widely.
- Performance issues: RMM agents can sometimes impact device performance. Optimize agent settings and ensure your network infrastructure can handle the increased traffic.
- Data security concerns: Address data security concerns by implementing strong authentication measures, encrypting data in transit and at rest, and regularly auditing security settings.
- Integration challenges: Integrating RMM with other IT tools can be complex. Choose RMM software that offers seamless integration with your existing systems and leverage APIs for data exchange.
RMM Monitoring Software for Different Industries
RMM monitoring software offers a comprehensive solution for managing and securing IT infrastructure across various industries. By providing a centralized platform for monitoring, managing, and automating tasks, RMM software helps businesses streamline operations, improve efficiency, and reduce downtime. Each industry faces unique challenges and requirements, and RMM software can be tailored to address these specific needs.
Healthcare
RMM monitoring software plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry, where patient data security and uptime are paramount. Healthcare providers rely on RMM software to:
- Ensure HIPAA Compliance: RMM software helps healthcare organizations meet HIPAA compliance requirements by providing tools for data encryption, access control, and audit logging.
- Secure Patient Data: RMM software safeguards patient data by monitoring network traffic, identifying vulnerabilities, and implementing security patches promptly.
- Maintain Uptime: RMM software helps healthcare providers maintain continuous operations by proactively monitoring critical systems, such as medical imaging equipment and electronic health records.
Finance
The financial industry demands high levels of security and compliance. RMM monitoring software addresses these needs by:
- Protecting Sensitive Data: RMM software helps financial institutions protect sensitive financial data by implementing multi-factor authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
- Ensuring Compliance: RMM software assists financial institutions in meeting regulatory requirements, such as PCI DSS and SOX, by providing audit trails and reporting features.
- Managing IT Infrastructure: RMM software simplifies IT infrastructure management for financial institutions by providing centralized monitoring, remote access, and automated patch management.
Education
Educational institutions rely on RMM monitoring software to support a variety of needs, including:
- Securing Student Data: RMM software protects student data from unauthorized access and cyber threats by implementing security measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems.
- Supporting Remote Learning: RMM software enables educational institutions to provide seamless remote learning experiences by monitoring and managing devices and applications used by students and teachers.
- Managing IT Infrastructure: RMM software helps educational institutions manage their IT infrastructure efficiently by providing centralized monitoring, automated patching, and remote access capabilities.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies rely on RMM monitoring software to ensure the reliability and security of their production processes. Key benefits include:
- Maintaining Production Uptime: RMM software helps manufacturers maintain production uptime by monitoring critical systems, such as manufacturing equipment and control systems, and proactively addressing potential issues.
- Improving Operational Efficiency: RMM software enables manufacturers to optimize their operations by providing insights into system performance, identifying bottlenecks, and automating tasks.
- Securing Industrial Control Systems: RMM software protects manufacturing companies from cyber threats by monitoring and securing industrial control systems, which are often vulnerable to attacks.
Future Trends in RMM Monitoring Software
The landscape of RMM monitoring software is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the changing needs of businesses. Emerging trends are shaping the future of RMM, offering enhanced capabilities and a more streamlined approach to IT management.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in RMM
AI is revolutionizing the way RMM software operates. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI can automate tasks, identify potential issues before they become problems, and provide predictive insights.
- Automated Incident Response: AI can analyze data from various sources, such as network logs and system performance metrics, to detect anomalies and automatically trigger pre-defined responses. For example, if a server is experiencing high CPU utilization, AI can automatically scale up resources or send alerts to IT staff.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data, AI can predict when hardware or software components are likely to fail, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime. For instance, AI can predict when a hard drive is nearing failure and trigger a replacement before it fails, preventing data loss.
- Security Threat Detection: AI can detect suspicious activities and potential security breaches in real time. It can analyze network traffic, identify unusual patterns, and flag potential threats, enabling faster and more efficient incident response.
Cloud-Based RMM Solutions
Cloud-based RMM solutions are gaining popularity due to their scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. These solutions offer several advantages over traditional on-premises software:
- Accessibility: Cloud-based RMM can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote monitoring and management of devices. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with a distributed workforce or multiple locations.
- Scalability: Cloud solutions can easily scale up or down to meet changing needs, eliminating the need for costly hardware upgrades. Businesses can add or remove devices as needed, without having to worry about server capacity or storage limitations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based RMM solutions typically have lower upfront costs compared to on-premises software. They also eliminate the need for hardware maintenance and software updates, further reducing overall costs.
Integration with Other IT Tools
Modern RMM software is designed to integrate seamlessly with other IT tools, creating a unified ecosystem for managing IT infrastructure. This integration allows for streamlined workflows and improved data sharing:
- Ticketing Systems: Integrating RMM with ticketing systems allows for automated incident reporting and tracking, improving communication and collaboration between IT teams and end users.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools: Integration with SIEM tools provides a centralized view of security events and threats across the network, enabling faster and more effective incident response.
- Remote Desktop Software: Integrating RMM with remote desktop software allows IT staff to access and control devices remotely, facilitating troubleshooting and support.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples: Rmm Monitoring Software
RMM monitoring software has been implemented by various businesses across industries, leading to improved IT efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced security. Real-world examples showcase the tangible benefits and challenges encountered during the implementation process.
Case Study: A Small Law Firm
A small law firm with a limited IT budget struggled with frequent system crashes and slow response times, impacting their productivity and client satisfaction. Implementing RMM monitoring software helped them proactively identify and resolve issues before they escalated. The software provided real-time performance data, enabling them to optimize system resources and ensure smooth operations. The firm also benefited from automated patch management, which reduced security vulnerabilities and minimized the risk of malware infections.
Case Study: A Large Healthcare Organization
A large healthcare organization with multiple locations faced challenges in managing a vast network of devices, ensuring HIPAA compliance, and responding quickly to security threats. Implementing RMM monitoring software enabled them to centrally monitor and manage all their devices, including workstations, servers, and mobile devices. The software provided comprehensive security features, including endpoint security, vulnerability scanning, and automated patching. This helped them meet HIPAA compliance requirements and mitigate security risks.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating RMM software with existing IT infrastructure can be challenging, requiring careful planning and configuration. Businesses need to ensure compatibility with existing systems and applications.
- User Training and Adoption: Successful implementation requires adequate user training and adoption. Providing comprehensive training and ongoing support is crucial to ensure that users are comfortable using the software and leveraging its full potential.
- Data Security and Privacy: Businesses need to prioritize data security and privacy when choosing and implementing RMM software. They should select software that meets industry standards and complies with relevant regulations.
Summary
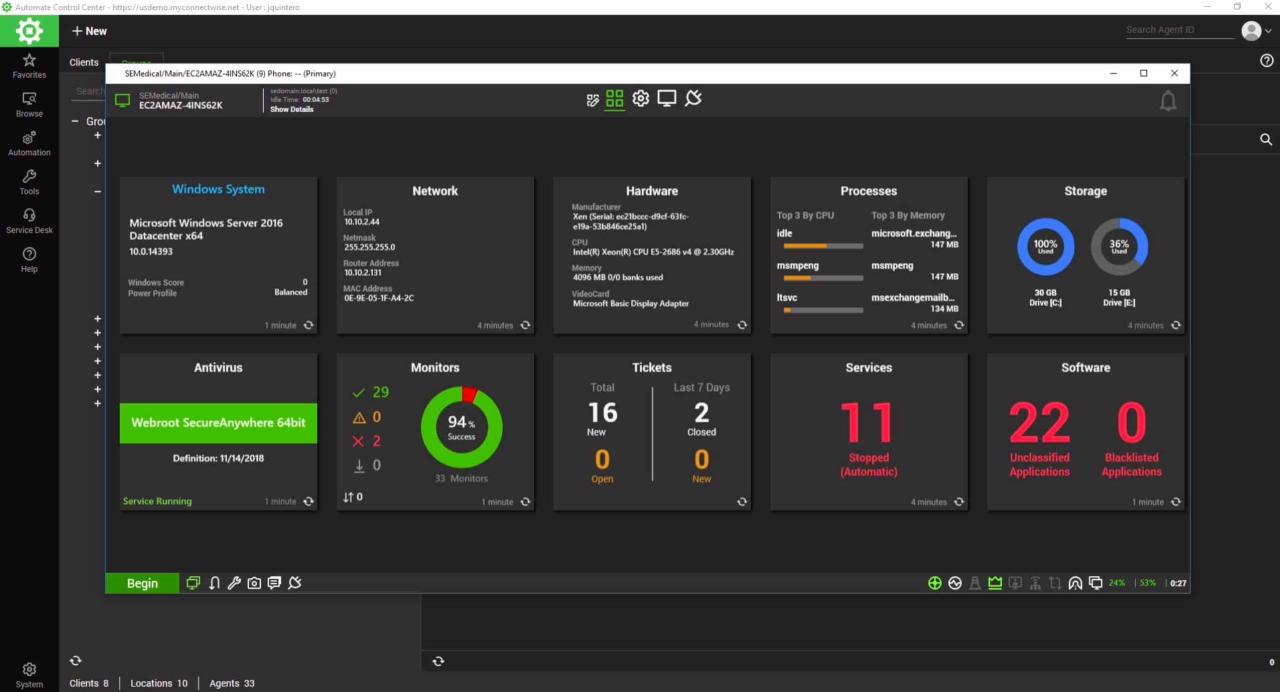
RMM monitoring software has become an indispensable tool for modern businesses, empowering IT teams to streamline operations, enhance security, and optimize productivity. By embracing this technology, organizations can gain a competitive edge, ensuring their IT infrastructure is secure, reliable, and future-proof. As RMM software continues to evolve, incorporating artificial intelligence and cloud-based solutions, it will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of IT management, offering businesses even greater efficiency and control.
RMM monitoring software provides valuable insights into the health and performance of your IT infrastructure. It helps you proactively identify and address issues before they impact users, saving time and resources. One concept that is particularly relevant to RMM is the time sharing operating system , which allows multiple users to share a single computer system simultaneously.
This concept, applied to RMM, means that the software can monitor and manage a large number of devices efficiently, maximizing resource utilization and ensuring smooth operation across your entire network.
