Remote management of a system allows individuals and organizations to control and monitor their systems from any location with an internet connection. This technology has revolutionized how we manage our digital assets, offering unprecedented flexibility and efficiency. Whether it’s accessing a home computer from across the globe, overseeing a server farm, or managing a network of devices, remote management has become an indispensable tool in today’s interconnected world.
Table of Contents
From the simplicity of accessing a personal computer remotely to the complex orchestration of large-scale data centers, remote management has become an integral part of modern technology. The ability to manage systems from anywhere allows for increased productivity, reduced downtime, and enhanced security.
Introduction to Remote System Management
Remote system management is the practice of controlling and managing computer systems and networks from a remote location. This approach eliminates the need for physical presence at the location of the system, enabling administrators to perform tasks such as monitoring, configuration, troubleshooting, and software updates from anywhere with an internet connection.
Remote system management is becoming increasingly significant in today’s digital landscape. Organizations rely on it to optimize their IT infrastructure, reduce operational costs, and enhance security. By enabling remote access, businesses can manage their systems more efficiently and effectively, regardless of geographical constraints.
Benefits of Remote System Management
The benefits of remote system management are numerous and can significantly impact an organization’s IT operations. Here are some key advantages:
- Improved Efficiency: Remote management allows administrators to access and manage multiple systems from a single location, streamlining operations and reducing the time required for routine tasks. This efficiency translates into cost savings and improved productivity.
- Enhanced Security: Remote access tools often incorporate robust security measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication, to protect sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access. This enhanced security helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and mitigate potential threats.
- Reduced Costs: By eliminating the need for on-site technicians, remote management reduces travel expenses, hardware costs, and other associated expenses. This cost reduction can be substantial, especially for organizations with geographically dispersed systems.
- Increased Availability: Remote access enables administrators to provide 24/7 support, ensuring continuous system uptime and minimizing downtime due to technical issues. This increased availability is crucial for businesses that rely on their systems for critical operations.
Challenges of Remote System Management
While remote system management offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges that organizations need to address. Here are some common challenges:
- Security Concerns: Remote access can create security vulnerabilities if not implemented properly. Organizations need to ensure that their remote management tools and systems are adequately secured to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. This involves implementing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits.
- Network Connectivity Issues: Remote management relies on stable and reliable network connectivity. Network outages or slow connections can disrupt operations and hinder the effectiveness of remote management. Organizations should invest in robust network infrastructure and consider backup solutions to mitigate the impact of connectivity issues.
- Technical Expertise: Effective remote management requires skilled administrators with the necessary technical expertise. Organizations need to invest in training and development programs to ensure their IT staff has the skills and knowledge to manage systems remotely.
- Complexity of Management: Managing multiple systems remotely can be complex, especially for large organizations with geographically dispersed IT infrastructure. Organizations need to implement effective management tools and processes to streamline operations and ensure efficient remote management.
Remote Management Technologies: Remote Management Of A System
Remote management technologies enable administrators to access and control systems remotely, facilitating efficient management and troubleshooting. These technologies offer a range of features, security measures, and usability characteristics, catering to diverse use cases.
SSH (Secure Shell)
SSH is a secure network protocol used for remote access to computer systems. It provides a secure channel for data transmission, ensuring confidentiality and integrity of data exchanged between the client and server.
SSH is commonly used for:
* Remote command execution: Administrators can execute commands on remote servers, enabling system administration tasks like installing software, configuring services, and managing files.
* Secure file transfer: SSH enables secure transfer of files between systems using the SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) protocol.
* Remote login: SSH provides a secure way to log in to remote systems, granting access to the user’s account and its associated resources.
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
RDP is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft for remote access to Windows systems. It allows users to connect to a remote computer and interact with its desktop environment as if they were physically present.
RDP is widely used for:
* Remote desktop access: Users can access and control their Windows desktop from a remote location, enabling them to work on their files, applications, and programs.
* Remote administration: Administrators can access and manage remote Windows systems, performing tasks like troubleshooting, software installation, and system configuration.
* Remote presentations: RDP facilitates sharing presentations and demonstrations with remote audiences, enabling interactive collaboration and communication.
VNC (Virtual Network Computing)
VNC is an open-source protocol that allows users to remotely control graphical desktop environments. It operates by capturing the screen of the remote computer and transmitting it to the client, enabling users to interact with the desktop as if they were directly connected.
VNC is often used for:
* Remote desktop access: VNC provides remote access to graphical desktop environments, allowing users to work on their computers from any location.
* Troubleshooting and support: VNC is useful for remotely assisting users with technical issues, enabling technicians to see and control the user’s desktop.
* Remote server management: VNC can be used to remotely manage servers with graphical interfaces, allowing administrators to configure and monitor the system.
Comparison of Technologies
| Technology | Features | Security | Usability | Use Cases |
|—|—|—|—|—|
| SSH | Secure command execution, file transfer, and remote login | Highly secure with encryption and authentication | Command-line based, requiring familiarity with terminal interfaces | System administration, secure file transfer, remote server management |
| RDP | Remote desktop access, remote administration, remote presentations | Less secure than SSH, requiring proper network configuration and strong passwords | Graphical user interface, intuitive for Windows users | Remote desktop access, remote administration, remote presentations |
| VNC | Remote desktop access, troubleshooting, remote server management | Security depends on implementation and configuration | Graphical user interface, easy to use | Remote desktop access, troubleshooting, remote server management |
Remote Monitoring and Management Tools

Remote monitoring and management tools are essential for organizations that need to keep their systems running smoothly and efficiently, regardless of location. These tools provide real-time visibility into system performance, health, and security, enabling administrators to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact users.
Popular Remote Management Tools
These tools offer a range of features and functionalities, making them suitable for various organizations and system sizes.
- Nagios: Nagios is a widely used open-source monitoring tool that provides comprehensive system and network monitoring capabilities. It can monitor various metrics, including CPU utilization, disk space, network traffic, and application performance. Nagios also offers alerting capabilities, notifying administrators of potential issues via email, SMS, or other methods.
- Zabbix: Zabbix is another popular open-source monitoring tool known for its scalability and flexibility. It supports a wide range of monitoring protocols, allowing it to monitor various systems, including servers, networks, databases, and applications. Zabbix provides real-time dashboards, historical data analysis, and customizable alerting mechanisms.
- SolarWinds: SolarWinds offers a suite of commercial monitoring and management tools, including Network Performance Monitor, Server & Application Monitor, and Database Performance Analyzer. These tools provide detailed insights into network performance, server health, and application behavior, helping organizations identify and resolve issues quickly.
Features and Functionalities of Remote Management Tools
Remote management tools offer a variety of features to streamline monitoring and management tasks.
- Real-time Monitoring: These tools provide real-time insights into system performance and health, allowing administrators to identify potential issues quickly. They often display key metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network traffic in dashboards or graphs.
- Alerting: Remote management tools can send alerts to administrators when predefined thresholds are breached or specific events occur. These alerts can be delivered via email, SMS, or other methods, ensuring timely notification of potential issues.
- Reporting: These tools often provide detailed reports on system performance, security events, and other relevant data. These reports can be used to identify trends, analyze performance bottlenecks, and improve system efficiency.
- Remote Control: Some remote management tools offer remote control capabilities, allowing administrators to access and manage systems remotely. This enables them to perform tasks like installing software, restarting services, or troubleshooting issues from a centralized location.
- Automation: Remote management tools can automate routine tasks, such as software updates, system backups, and security scans. This frees up administrators’ time and reduces the risk of human error.
Facilitating Remote Monitoring and Management
Remote monitoring and management tools provide a centralized platform for managing systems, regardless of location.
- Centralized Visibility: These tools provide a unified view of all monitored systems, allowing administrators to easily assess their overall health and performance. This eliminates the need to manually check individual systems, saving time and effort.
- Proactive Issue Resolution: By providing real-time insights and alerts, remote management tools enable administrators to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact users. This helps minimize downtime and ensure continuous system availability.
- Improved Efficiency: Remote management tools automate routine tasks, freeing up administrators’ time to focus on more strategic initiatives. This increases overall efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Security: These tools can help organizations improve security by monitoring system events, detecting anomalies, and enforcing security policies. They can also automate security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning and patch management.
Security Considerations for Remote Management
Remote system management, while offering numerous advantages, also presents significant security risks. These risks arise from the inherent vulnerabilities associated with remote access and data transfer. It is crucial to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access to managed systems.
Best Practices for Securing Remote Access and Data
Securing remote access and data involves implementing a comprehensive set of best practices to minimize vulnerabilities and protect sensitive information. These practices encompass a multi-layered approach that addresses various aspects of remote management.
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code generated by a mobile app or hardware token. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
- Secure Communication Protocols: Utilize secure communication protocols, such as Secure Shell (SSH) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS), to encrypt data transmitted between the management console and the remote system. Encryption ensures that data remains confidential and protected from eavesdropping or interception.
- Access Control: Implement granular access control mechanisms to restrict user permissions based on their roles and responsibilities. This principle of least privilege ensures that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their tasks, minimizing the potential for unauthorized actions.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in the remote management system. These audits should include assessments of access controls, authentication mechanisms, communication protocols, and system configurations. Regular audits help to ensure that security measures remain effective and address emerging threats.
- Security Awareness Training: Provide security awareness training to all users who access the remote management system. Training should cover best practices for secure password management, recognizing phishing attempts, and reporting suspicious activities. Educating users about security threats and best practices helps to reduce the risk of human error.
Methods for Mitigating Security Vulnerabilities
Mitigating security vulnerabilities in remote management involves implementing proactive measures to address potential weaknesses and prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all software components of the remote management system, including operating systems, applications, and security tools, up-to-date with the latest security patches. Software updates often include fixes for known vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of exploitation.
- Firewall Configuration: Configure firewalls to block unauthorized access to the remote management system. Firewalls act as a barrier between the system and the external network, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on defined rules. Proper firewall configuration helps to prevent unauthorized connections and attacks.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor network traffic for malicious activity and block suspicious connections. IDPS can identify and respond to attacks in real-time, reducing the impact of security breaches.
- Regular Security Testing: Conduct regular penetration testing to assess the security posture of the remote management system. Penetration testing involves simulating real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors. Regular testing helps to ensure that security measures are effective and identify areas for improvement.
Remote Management in Different Environments
Remote management is essential in various environments, each presenting unique challenges and requiring tailored solutions. This section explores the specific considerations and applications of remote management in cloud computing, data centers, and home networks.
Remote Management in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing environments, characterized by their dynamic and scalable nature, pose specific challenges for remote management.
– Dynamic Infrastructure: The constant changes in resources, such as virtual machines and containers, require flexible and automated remote management tools.
– Scalability: The ability to manage a large number of resources across multiple cloud providers necessitates efficient and centralized management solutions.
– Security: Ensuring secure access and data protection in a distributed cloud environment is crucial.
Remote management solutions for cloud computing often employ:
– Cloud Management Platforms (CMPs): These platforms provide centralized control and visibility over cloud resources, enabling tasks such as provisioning, monitoring, and security management.
– Configuration Management Tools: Tools like Ansible and Puppet automate configuration and deployment of cloud resources, ensuring consistency and reducing manual errors.
– API Integration: Leveraging cloud provider APIs enables seamless integration of remote management tools with cloud services.
- Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a comprehensive suite of tools for remote management, including AWS Management Console, AWS CloudFormation, and AWS CloudTrail.
Remote Management in Data Centers
Data centers, with their large-scale infrastructure and critical workloads, require robust and reliable remote management solutions.
– Physical Infrastructure: Managing physical servers, network devices, and storage systems remotely requires specialized tools and protocols.
– High Availability: Ensuring uninterrupted service and minimizing downtime is critical in data center environments.
– Security: Data centers house sensitive information, demanding stringent security measures for remote access and data protection.
Remote management in data centers typically involves:
– Remote Monitoring and Management Tools: These tools provide real-time visibility into data center operations, allowing administrators to monitor performance, identify issues, and take corrective actions remotely.
– Out-of-Band Management: This approach enables remote access to devices even when they are not powered on, facilitating troubleshooting and recovery in case of outages.
– Automated Tasks: Scripting and automation tools help streamline repetitive tasks, such as server provisioning and software updates, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
- Example: Data center operators often use solutions like SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor and Datadog for remote monitoring and management.
Remote Management in Home Networks, Remote management of a system
While less complex than data centers or cloud environments, home networks still benefit from remote management capabilities.
– Device Management: Managing connected devices, such as computers, printers, and smart home appliances, remotely can enhance convenience and troubleshooting.
– Security: Protecting home networks from cyber threats requires remote access for security updates, malware removal, and firewall configuration.
– Remote Access: Enabling remote access to home computers or servers can be useful for work, entertainment, or accessing files while away from home.
Remote management solutions for home networks often include:
– Remote Desktop Software: Tools like TeamViewer and AnyDesk allow users to control their home computers remotely.
– Network Management Software: Applications like Netgear Genie and Linksys Smart Wi-Fi provide a centralized interface for managing network settings, monitoring devices, and troubleshooting connectivity issues.
– Cloud-Based Services: Some services, such as Google Nest Hub and Amazon Echo, offer remote management capabilities for smart home devices.
- Example: A homeowner can use a remote desktop software to access their home computer while on vacation to check emails or download files.
Future Trends in Remote Management
The landscape of remote system management is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Emerging technologies and trends are reshaping how organizations manage their systems remotely, offering new opportunities for efficiency, scalability, and security. This section explores some of the key trends that will shape the future of remote management.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing remote management by automating tasks, optimizing performance, and improving security. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data from remote systems to identify patterns, predict potential issues, and proactively address them. ML algorithms can learn from historical data to optimize resource allocation, automate routine tasks, and enhance security by detecting anomalies and threats.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered systems can analyze sensor data and historical maintenance records to predict when equipment is likely to fail, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Automated Incident Response: AI can analyze security logs and network traffic to detect and respond to threats in real time, minimizing the impact of cyberattacks.
- Performance Optimization: AI can analyze system performance metrics to identify bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation, improving overall system efficiency.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings processing power closer to the source of data, reducing latency and improving performance for remote systems. This trend is particularly relevant for applications that require real-time data processing, such as IoT devices, industrial automation, and remote healthcare. Edge computing enables faster response times, reduced bandwidth consumption, and enhanced data security by keeping sensitive data closer to its source.
Cloud-Native Technologies
Cloud-native technologies are designed to run in cloud environments, offering scalability, flexibility, and agility for remote management. These technologies, such as containers and microservices, enable organizations to deploy and manage applications and infrastructure more efficiently, regardless of location. Cloud-native platforms provide a robust foundation for remote management, facilitating rapid deployment, seamless scaling, and simplified maintenance.
The Rise of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The increasing adoption of IoT devices is driving the need for more sophisticated remote management solutions. Managing a vast network of connected devices requires robust tools and processes to ensure security, performance, and reliability. Remote management platforms are evolving to support the unique challenges of managing IoT devices, including data collection, device provisioning, and security updates.
The Importance of Cybersecurity
As remote management becomes more prevalent, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Organizations must prioritize security measures to protect their systems from cyberattacks and data breaches. This includes implementing strong authentication mechanisms, encrypting data in transit and at rest, and using intrusion detection and prevention systems. The future of remote management will be characterized by a strong focus on security, with organizations adopting proactive measures to mitigate risks and protect their critical systems.
Examples of Remote Management Applications

Remote management has become ubiquitous across various industries, revolutionizing how businesses operate and manage their IT infrastructure. From monitoring and controlling critical systems to automating tasks and ensuring security, remote management offers numerous advantages, enabling organizations to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
Applications Across Industries
Remote management applications are found in various industries, each with specific requirements and benefits. The following table showcases some common examples:
| Industry | Specific Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare |
|
|
| Finance |
|
|
| Manufacturing |
|
|
| Retail |
|
|
| Education |
|
|
Case Studies of Successful Remote Management
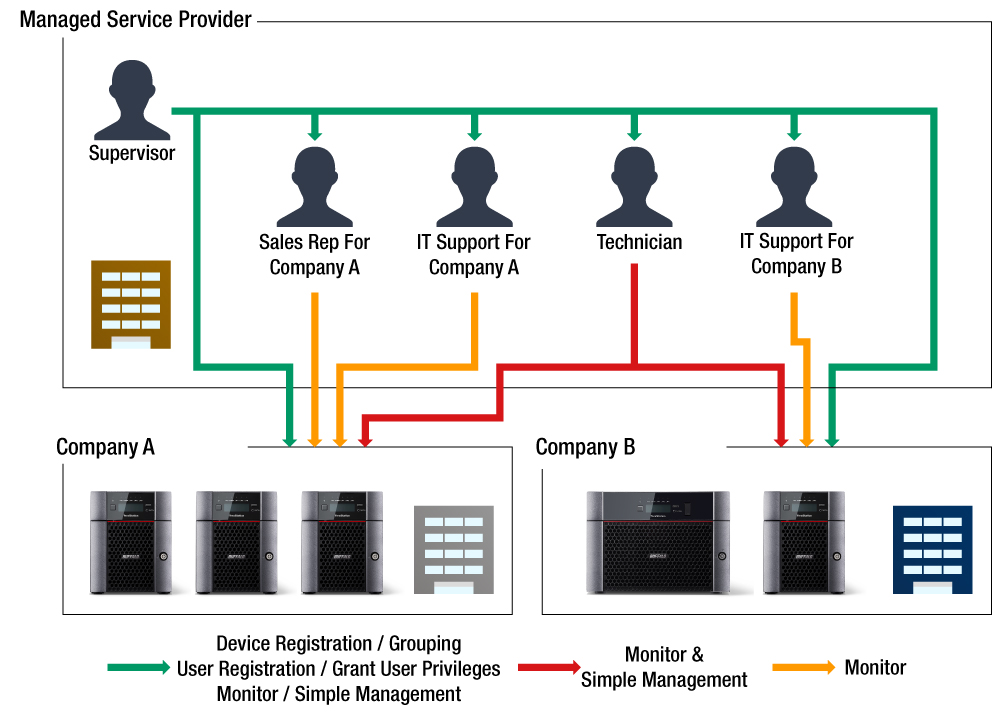
Real-world examples of successful remote system management implementations demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach. These case studies showcase the challenges faced by organizations, the solutions implemented, and the positive impact on their operations.
Remote Management for Global Financial Services
This case study examines how a global financial services company leveraged remote management to streamline its IT operations across multiple continents. The organization faced several challenges, including:
* Managing a geographically dispersed IT infrastructure: The company had data centers and offices in various countries, making it difficult to manage and maintain its IT systems effectively.
* Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements: The financial services industry is heavily regulated, and the company needed to ensure its IT systems met all compliance standards.
* Minimizing downtime and maximizing system availability: Any downtime in the company’s IT systems could result in significant financial losses, so ensuring high availability was crucial.
To address these challenges, the company implemented a comprehensive remote management solution that included:
* Centralized monitoring and management platform: This platform allowed the company to monitor and manage its IT systems from a single location, regardless of their physical location.
* Automated provisioning and configuration: This feature streamlined the process of setting up new systems and configuring them to meet the company’s specific requirements.
* Remote troubleshooting and support: The company’s IT staff could remotely diagnose and resolve issues, reducing the need for on-site visits.
The implementation of remote management resulted in several benefits for the financial services company, including:
* Improved efficiency and productivity: The company’s IT staff could manage more systems with fewer resources, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
* Reduced operational costs: Remote management reduced the need for on-site visits and travel expenses, resulting in significant cost savings.
* Enhanced security and compliance: The centralized monitoring and management platform enabled the company to enforce security policies and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
* Increased system availability: Remote troubleshooting and support minimized downtime and ensured high system availability.
This case study demonstrates the value of remote management for organizations with geographically dispersed IT infrastructures. By implementing a comprehensive solution, the financial services company achieved significant improvements in efficiency, cost savings, security, and system availability.
Best Practices for Implementing Remote Management
Implementing remote management effectively requires careful planning and adherence to best practices. These practices ensure security, reliability, and optimal performance of your systems while enabling efficient remote access and control.
Planning and Design
Planning and designing your remote management system is crucial for its success. A well-defined strategy ensures a secure, reliable, and efficient system that meets your organization’s needs.
- Define Clear Objectives and Scope: Clearly define the objectives and scope of your remote management system. Identify the specific systems, devices, and functionalities you want to manage remotely. This helps determine the necessary resources, technologies, and security measures. For example, if you’re managing a network of servers, your objectives might include monitoring performance, managing updates, and troubleshooting issues remotely.
- Conduct a Thorough Security Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive security assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and risks associated with remote management. This includes assessing network security, access control mechanisms, and data encryption protocols. For instance, a security assessment might reveal weaknesses in your network’s firewall configuration, requiring adjustments to strengthen security.
- Choose the Right Technologies: Select appropriate technologies for your remote management system based on your specific requirements, budget, and existing infrastructure. Consider factors such as scalability, security features, compatibility with your systems, and ease of use. For example, if you need to manage a large number of devices across different locations, a cloud-based remote management solution might be more suitable than an on-premises solution.
- Implement a Robust Access Control System: Establish a robust access control system that limits access to authorized personnel and restricts permissions based on roles and responsibilities. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. For instance, you can implement multi-factor authentication to require users to provide multiple forms of identification before granting access to the system.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount when implementing remote management. Strong security measures protect your systems and data from unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
- Use Strong Authentication and Authorization: Implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to verify user identities and prevent unauthorized access. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code generated by a mobile app, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access.
- Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect it from interception and unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. For instance, use Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt data transmitted over the network and employ encryption algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) to encrypt data stored on servers or devices.
- Regularly Update Software and Security Patches: Regularly update software and security patches for your remote management tools and the systems you are managing. This helps mitigate vulnerabilities and protect against known security threats. Keep track of software updates and security patches released by vendors and apply them promptly to ensure your systems remain secure.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Segment your network to isolate your remote management systems and data from other parts of your network. This limits the impact of a security breach and prevents attackers from gaining access to sensitive data. For example, create a separate network segment for your remote management servers and restrict access to only authorized personnel.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Continuous monitoring and regular maintenance are essential for ensuring the smooth operation and security of your remote management system.
- Implement Comprehensive Monitoring: Implement comprehensive monitoring tools to track the performance, health, and security of your remote management system and the devices you are managing. This allows you to detect issues promptly and take corrective actions before they escalate. For example, monitor system logs, performance metrics, and security events to identify anomalies or potential threats.
- Perform Regular System Audits: Conduct regular audits of your remote management system to assess its security posture, compliance with regulations, and adherence to best practices. This helps identify vulnerabilities, security gaps, and areas for improvement. For instance, you can perform penetration testing to simulate attacks and identify weaknesses in your system’s security.
- Establish Clear Responsibilities: Establish clear responsibilities for managing, maintaining, and troubleshooting your remote management system. This ensures accountability and efficient problem resolution. For example, assign specific roles and responsibilities to individuals or teams for monitoring, security updates, and troubleshooting.
- Develop a Disaster Recovery Plan: Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in case of unexpected events, such as natural disasters or cyberattacks. This plan should Artikel procedures for restoring system functionality and data in a timely and secure manner. For example, create backups of your remote management system and data and test your disaster recovery plan regularly to ensure its effectiveness.
Closure
The future of remote management is bright, with advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and automation promising to further enhance its capabilities. As we continue to rely on technology to connect and operate, the ability to manage systems remotely will become even more crucial. From streamlining IT operations to empowering remote workforces, remote management is poised to transform the way we interact with and control our digital world.
Remotely managing a system can be a challenge, especially when dealing with large amounts of data. If you need to extract audio from a video for a presentation or simply to listen to it on the go, consider using a video to mp3 converter.
This can help reduce file size and make the data more manageable for remote access and processing.
