Gartner Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) has become a cornerstone of modern IT management, offering organizations the ability to oversee and control their technology infrastructure from anywhere in the world. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of RMM, exploring its definition, benefits, key features, and the critical role it plays in ensuring business continuity and cybersecurity.
Table of Contents
From traditional IT management to cloud-based solutions, RMM has evolved significantly, adapting to the changing landscape of technology and the increasing demand for remote accessibility and proactive management. This guide examines the key features of modern RMM solutions, including remote access, patch management, endpoint security, and system monitoring, highlighting how these capabilities contribute to a robust cybersecurity posture and enhanced IT performance.
RMM and Cybersecurity
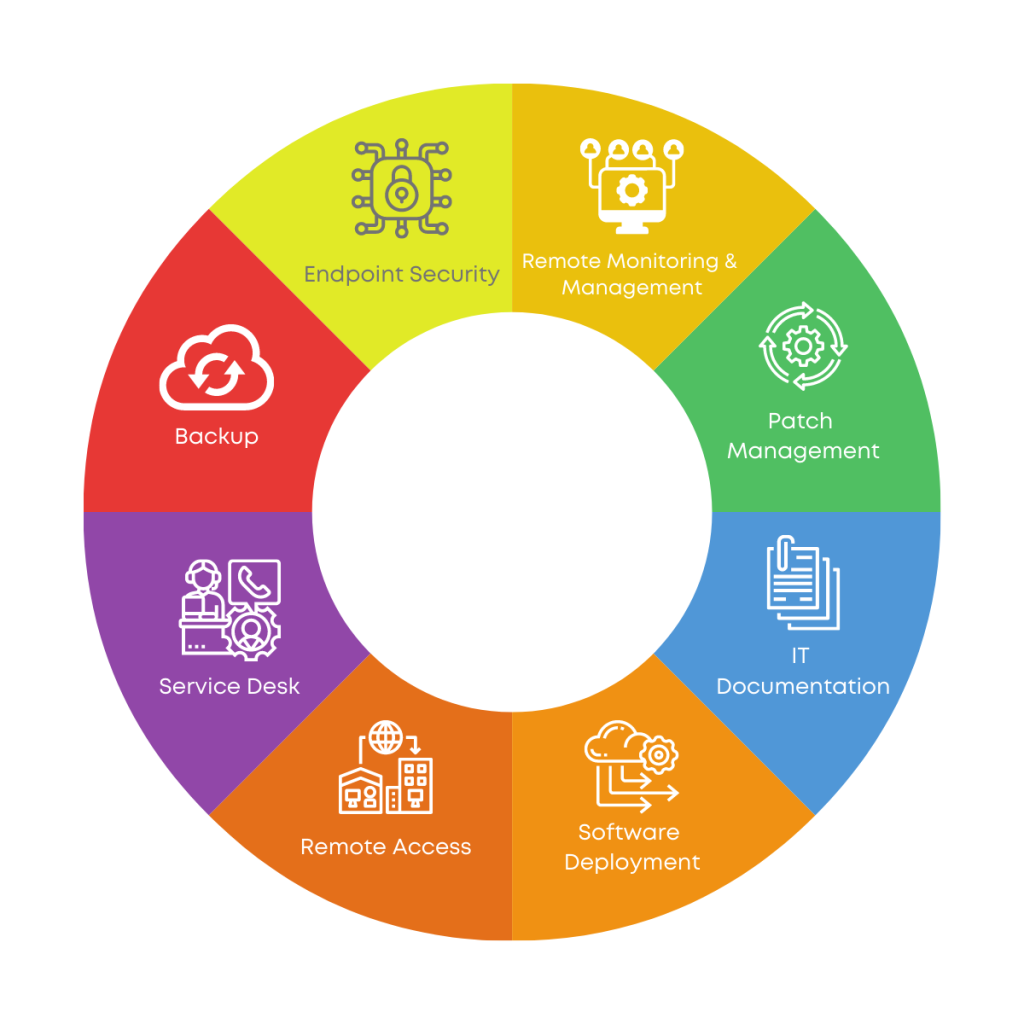
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions play a vital role in bolstering cybersecurity by providing a centralized platform for managing and securing endpoints.
RMM and Enhanced Cybersecurity Posture
RMM solutions contribute to a robust cybersecurity posture by enabling proactive security measures, simplifying vulnerability management, and automating security tasks. RMM tools can:
- Automate Patch Management: RMM automates the process of patching vulnerabilities in operating systems, applications, and software, ensuring that systems are updated with the latest security patches. This reduces the risk of exploits targeting known vulnerabilities.
- Implement Security Policies: RMM platforms allow administrators to enforce security policies across endpoints, including password complexity requirements, firewall configurations, and access control restrictions. This helps to prevent unauthorized access and malware infections.
- Monitor Endpoint Security: RMM solutions provide real-time visibility into endpoint security status, including antivirus protection, firewall status, and system logs. This allows administrators to quickly identify and respond to security threats.
RMM and Threat Detection and Response
RMM plays a crucial role in detecting and responding to security threats by providing early warning systems, automating incident response, and facilitating rapid remediation.
- Real-Time Threat Detection: RMM tools monitor endpoints for suspicious activity, including malware infections, unauthorized access attempts, and unusual network traffic. This enables early detection of threats before they can cause significant damage.
- Automated Incident Response: RMM platforms can automate incident response actions, such as isolating infected devices, quarantining malicious files, and triggering alerts to security teams. This streamlines the incident response process and minimizes downtime.
- Rapid Remediation: RMM tools facilitate rapid remediation of security threats by providing access to remote control capabilities, allowing administrators to quickly address vulnerabilities and remove malware. This reduces the impact of security incidents and minimizes business disruption.
RMM and Security Policy Enforcement
RMM solutions can be used to enforce security policies and protect sensitive data by providing a centralized platform for managing and enforcing security controls across endpoints.
- Password Management: RMM tools can enforce password complexity requirements, ensuring that users create strong passwords that are difficult to guess. This helps to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Data Encryption: RMM solutions can encrypt sensitive data stored on endpoints, making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals. This helps to protect sensitive information from theft or unauthorized access.
- Access Control: RMM platforms can restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can access specific information. This helps to prevent data breaches and unauthorized data disclosure.
Implementation and Deployment of RMM
Implementing an RMM solution is a strategic move to enhance your organization’s IT security and management capabilities. It requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition and maximize its benefits.
Step-by-Step Guide for Implementing an RMM Solution
A structured approach is crucial for successful RMM implementation. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
- Needs Assessment: Identify your specific IT management and security needs. This includes understanding your current infrastructure, potential vulnerabilities, and desired outcomes.
- Solution Selection: Research and evaluate various RMM solutions based on your needs and budget. Consider factors like features, pricing, compatibility, and user-friendliness.
- Pilot Deployment: Before a full-scale rollout, conduct a pilot implementation on a small group of devices. This allows you to test the solution, identify any potential issues, and refine your deployment strategy.
- Configuration and Customization: Configure the RMM solution to match your organization’s specific requirements. This involves setting up policies, alerts, and reporting mechanisms.
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training to your IT staff on using the RMM solution effectively. This includes hands-on exercises and practical scenarios.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly monitor the RMM solution’s performance and make necessary adjustments to optimize its effectiveness. This includes reviewing reports, identifying trends, and implementing improvements.
Considerations for Integrating RMM with Existing IT Infrastructure
Integrating RMM with your existing IT infrastructure requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations:
- Compatibility: Ensure the RMM solution is compatible with your existing operating systems, hardware, and software.
- Network Security: Address network security concerns related to data transfer and access control. Implement appropriate firewalls and security protocols.
- Data Integration: Determine how to integrate RMM data with your existing systems for reporting and analysis. Consider using APIs or other integration methods.
- User Permissions: Establish clear user permissions and access control to ensure data security and prevent unauthorized access.
Best Practices for Training IT Staff on Using the RMM Solution Effectively
Effective training is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your RMM solution. Here are some best practices:
- Hands-on Training: Provide hands-on training that allows staff to practice using the RMM solution in real-world scenarios.
- Scenario-Based Learning: Develop training modules that simulate common IT management and security challenges.
- Regular Refresher Training: Conduct regular refresher training sessions to ensure staff stay up-to-date with the latest features and best practices.
- Documentation and Resources: Provide comprehensive documentation, user guides, and online resources for ongoing reference.
- Support and Assistance: Offer ongoing support and assistance to staff who encounter difficulties or have questions.
RMM and the Future of IT Management
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions are undergoing a rapid evolution, driven by the increasing complexity of IT environments and the need for greater automation and efficiency. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is transforming the way RMM tools operate, leading to a more proactive and intelligent approach to IT management.
The Role of AI and ML in RMM
AI and ML are transforming RMM by enabling more intelligent and automated IT management. These technologies are used to analyze vast amounts of data from IT systems, identify patterns and anomalies, and predict potential problems before they occur. This proactive approach to IT management helps organizations reduce downtime, improve performance, and optimize costs.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI and ML algorithms can analyze historical data on system performance and usage patterns to identify potential hardware failures and predict when maintenance is required. This allows organizations to schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime and reducing the risk of unexpected outages.
- Automated Incident Response: AI-powered RMM solutions can automate incident response by identifying and resolving common issues automatically. This frees up IT staff to focus on more complex tasks, improving efficiency and reducing the time it takes to resolve issues.
- Security Threat Detection: AI and ML algorithms can analyze network traffic and system logs to identify suspicious activity and potential security threats. This allows organizations to detect and respond to threats more quickly, reducing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Evolving RMM Solutions
Modern RMM solutions are evolving to meet the demands of today’s complex IT environments. This includes the integration of cloud-based services, enhanced security features, and support for a wider range of devices and operating systems.
- Cloud-Based RMM: Cloud-based RMM solutions offer greater scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to manage IT systems from anywhere with an internet connection. This also reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure, lowering costs and simplifying deployment.
- Enhanced Security: Modern RMM solutions include advanced security features such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. This helps organizations protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access to IT systems.
- Cross-Platform Support: RMM solutions are now supporting a wider range of devices and operating systems, including desktops, laptops, servers, mobile devices, and cloud infrastructure. This allows organizations to manage their entire IT infrastructure from a single platform.
Predictions for the Future of RMM
The future of RMM is bright, with the continued integration of AI and ML driving further innovation and efficiency. As IT environments become even more complex, RMM solutions will play a crucial role in helping organizations manage their systems effectively.
- Increased Automation: AI and ML will enable even greater automation in RMM, automating tasks such as patch management, software updates, and system configuration. This will free up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives and innovation.
- Proactive Security: RMM solutions will become more proactive in identifying and mitigating security threats. AI and ML will enable real-time threat detection and response, minimizing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
- Personalized IT Management: RMM solutions will be able to tailor their management strategies to the specific needs of each organization. This will involve using AI and ML to analyze data on system usage and performance, identifying areas where optimization is possible.
Case Studies of RMM Success
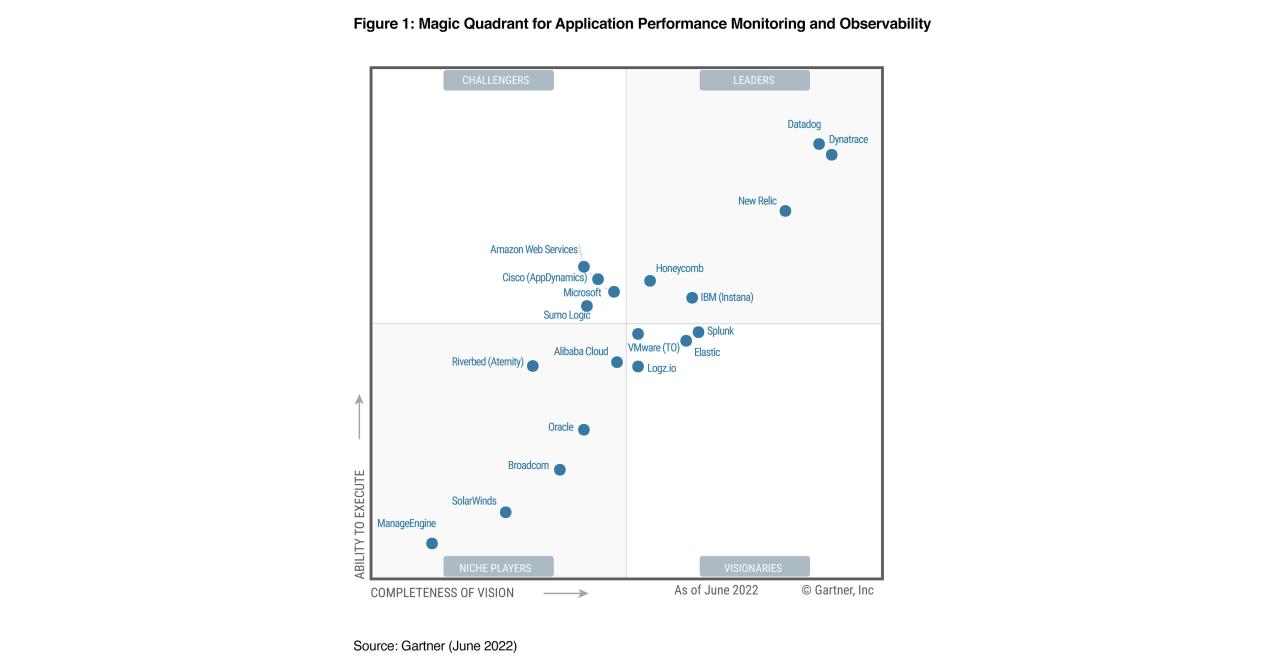
Real-world examples demonstrate the transformative power of RMM solutions. By examining successful implementations, we can gain insights into the tangible benefits organizations have achieved, including improved security, efficiency, and cost savings.
Case Study: A Healthcare Organization
This healthcare organization, with multiple locations and a large number of devices, faced significant challenges in managing its IT infrastructure. They were struggling with slow response times, security vulnerabilities, and high maintenance costs. To address these challenges, they implemented an RMM solution. The RMM solution enabled them to automate routine tasks, such as software updates and patch management, freeing up their IT team to focus on more strategic initiatives. It also provided real-time monitoring of devices, allowing them to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impacted patient care.
- Improved Security: The RMM solution’s automated patch management and vulnerability scanning capabilities significantly reduced the organization’s attack surface, minimizing the risk of cyberattacks.
- Increased Efficiency: By automating routine tasks, the IT team gained valuable time to focus on more strategic projects, such as implementing new technologies and improving patient care.
- Reduced Costs: The RMM solution’s proactive approach to maintenance and support reduced the number of incidents requiring costly on-site visits.
Case Study: A Financial Institution
A financial institution with a global presence was facing significant challenges in managing its IT infrastructure across multiple locations and time zones. They were struggling with security vulnerabilities, slow response times, and high maintenance costs. To address these challenges, they implemented an RMM solution.
- Enhanced Security: The RMM solution’s automated patch management and vulnerability scanning capabilities enabled the financial institution to proactively identify and remediate security vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of data breaches and financial losses.
- Improved Efficiency: The RMM solution’s remote access capabilities allowed the IT team to provide support to users across multiple locations, regardless of their time zone, minimizing downtime and improving productivity.
- Reduced Costs: By automating routine tasks and providing remote support, the RMM solution reduced the need for costly on-site visits, resulting in significant cost savings.
RMM and Compliance
In today’s data-driven world, organizations face a growing number of compliance requirements designed to protect sensitive information and ensure data security. Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solutions play a crucial role in helping organizations achieve and maintain compliance by providing the necessary tools and automation to manage IT infrastructure effectively and securely.
RMM and Compliance Standards
RMM solutions can assist organizations in meeting various industry-specific compliance standards, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for healthcare and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) for businesses handling credit card information. These standards mandate specific security controls and best practices that organizations must implement and maintain.
- HIPAA: This standard focuses on protecting patient health information (PHI). RMM tools can help organizations meet HIPAA requirements by providing features such as:
- Access control and auditing: RMM solutions can enforce strong password policies and track user activity, ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Data encryption: RMM tools can automatically encrypt data at rest and in transit, safeguarding PHI from unauthorized access.
- Vulnerability scanning: RMM solutions can regularly scan for vulnerabilities in systems and applications, identifying potential security risks and allowing for timely remediation.
- PCI DSS: This standard focuses on protecting credit card data. RMM tools can help organizations meet PCI DSS requirements by providing features such as:
- Network segmentation: RMM solutions can help organizations segment their networks to isolate sensitive data from other systems, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Firewall management: RMM tools can help organizations configure and manage firewalls effectively, blocking unauthorized access to critical systems and data.
- Regular security assessments: RMM solutions can automate security assessments, ensuring that systems and applications meet PCI DSS compliance requirements.
Challenges and Considerations: Gartner Remote Monitoring And Management
While RMM solutions offer significant advantages, their implementation and use can come with certain challenges. It’s crucial to acknowledge these challenges and implement strategies to mitigate them to maximize the benefits of RMM.
Challenges in Implementing and Using RMM Solutions
Implementing and using RMM solutions effectively involves addressing several challenges, including:
- Initial Setup and Configuration: The initial setup and configuration of an RMM solution can be complex, requiring technical expertise and time. This involves integrating the RMM software with existing infrastructure, configuring policies, and training users.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating the RMM solution with existing IT systems, such as Active Directory or ticketing systems, can be challenging. Ensuring compatibility and seamless data flow is crucial for optimal performance.
- Security Concerns: RMM solutions handle sensitive data, so ensuring the security of the platform and the data it manages is paramount. This involves implementing robust security measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication.
- Cost Considerations: RMM solutions can come with recurring subscription fees and potentially additional costs for implementation and support. Carefully evaluating the cost-benefit analysis is crucial before making a decision.
- User Adoption and Training: User adoption and training are critical for successful RMM implementation. Providing adequate training and support to users can help them understand and utilize the RMM solution effectively.
- Performance and Scalability: As the number of managed devices grows, the RMM solution needs to be scalable and performant. Performance issues can arise if the solution is not adequately designed for scalability.
Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance
Ongoing monitoring and maintenance of the RMM system are essential for ensuring its effectiveness and maximizing its benefits. This involves:
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitoring the RMM system for performance, security, and operational issues is critical. This can involve checking logs, monitoring alerts, and reviewing system health metrics.
- Software Updates and Patches: Keeping the RMM software and its components up-to-date with the latest patches and updates is essential for security and performance. This helps mitigate vulnerabilities and ensures compatibility with evolving technologies.
- Regular Backups: Implementing regular backups of the RMM system and its data is crucial for disaster recovery. This ensures that the system can be restored in case of data loss or system failure.
- Performance Tuning: As the number of managed devices increases, the RMM system may require performance tuning to ensure optimal operation. This can involve optimizing system configurations, adjusting resource allocation, and ensuring sufficient hardware resources.
- Security Audits: Regular security audits of the RMM system are essential for identifying and mitigating potential vulnerabilities. This involves reviewing security configurations, testing security controls, and assessing potential risks.
Recommendations for Mitigating Challenges and Maximizing Benefits, Gartner remote monitoring and management
Several strategies can help mitigate challenges and maximize the benefits of RMM solutions:
- Thorough Planning and Assessment: Before implementing an RMM solution, it’s essential to conduct a thorough assessment of your organization’s needs and requirements. This involves identifying the scope of the solution, defining key objectives, and considering potential challenges.
- Choosing the Right Solution: Selecting the right RMM solution is crucial. Carefully evaluate different solutions based on features, functionality, pricing, and support options. Consider factors like scalability, integration capabilities, and security features.
- Pilot Implementation: Consider a pilot implementation before full-scale deployment to test the solution and identify potential issues. This allows you to refine the configuration, optimize performance, and ensure user adoption before rolling out the solution across the organization.
- Proper Training and Support: Providing adequate training and ongoing support to users is essential for successful adoption. This includes training on the features and functionality of the RMM solution, troubleshooting guides, and ongoing support channels.
- Regular Monitoring and Maintenance: Establish a comprehensive monitoring and maintenance plan to ensure the ongoing effectiveness of the RMM solution. This includes regular monitoring for performance, security, and operational issues, software updates and patches, regular backups, and performance tuning.
Final Review
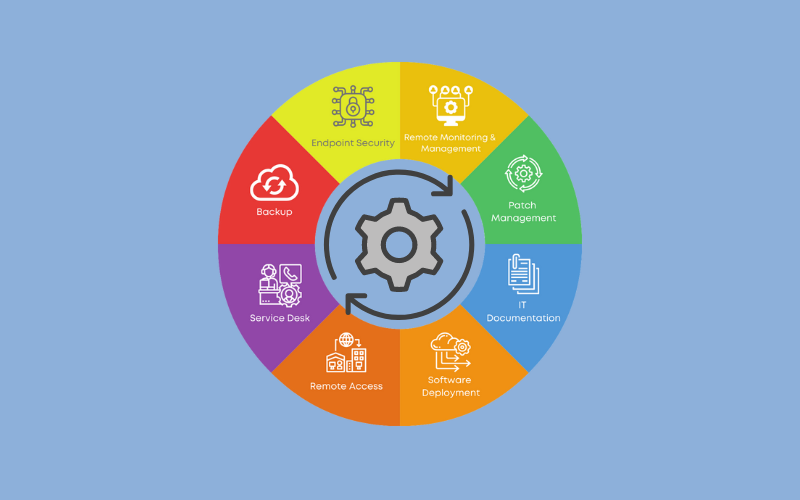
Ultimately, embracing Gartner Remote Monitoring and Management empowers organizations to optimize their IT operations, enhance security, and drive efficiency. By understanding the benefits, features, and implementation strategies of RMM, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of modern IT management and position themselves for success in the digital age.
Gartner’s research on remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools often highlights the importance of secure and reliable platforms. For example, a robust forum software like phpbb can be a valuable asset for RMM vendors, allowing them to connect with users and provide support, fostering a strong sense of community.
This community engagement can ultimately contribute to the overall success of an RMM solution.
