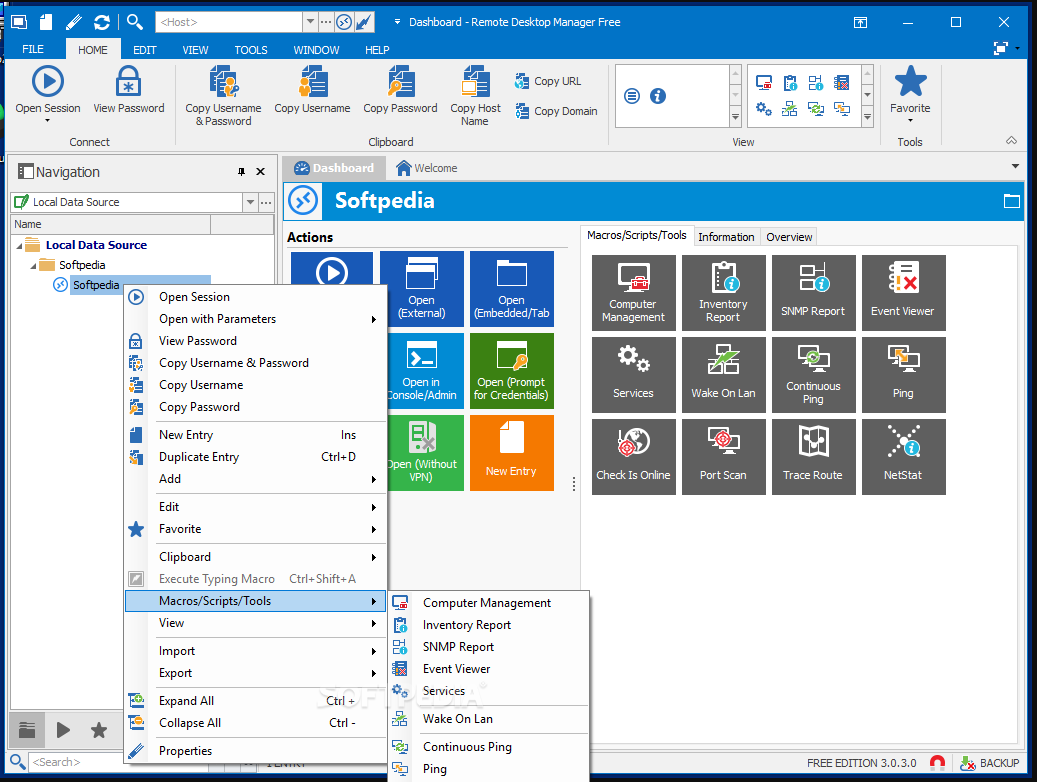
Remote management tools have revolutionized how we manage and control our digital assets, empowering businesses and individuals to streamline operations, enhance security, and boost productivity. From managing servers and networks to remotely controlling devices and accessing data, these tools have become indispensable in today’s interconnected world.
Table of Contents
Remote management tools offer a range of functionalities, from basic remote access to advanced automation and security features. They enable us to work from anywhere, access critical resources securely, and maintain a consistent level of control over our digital infrastructure, regardless of location.
Introduction to Remote Management Tools
Remote management tools are software applications that allow users to control and manage computer systems, networks, and devices from a remote location. These tools are essential for businesses and organizations that need to monitor and manage their IT infrastructure remotely, especially in today’s increasingly distributed and mobile work environments.
Remote management tools have evolved significantly over time, from simple command-line utilities to sophisticated web-based platforms that offer a wide range of features and functionalities. Early remote management tools focused on basic tasks such as remote access and file transfer, while modern tools provide comprehensive capabilities for system administration, security management, and network monitoring.
Examples of Remote Management Tools in Various Industries
Remote management tools are widely used across various industries, enabling organizations to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance security. Here are some examples:
- IT Management: System administrators use remote management tools to manage servers, workstations, and other devices across geographically dispersed locations. They can perform tasks such as installing software, configuring settings, and troubleshooting issues remotely, minimizing downtime and improving productivity.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics use remote management tools to manage medical devices, such as imaging equipment and patient monitoring systems. These tools allow healthcare professionals to monitor patient data remotely, diagnose issues, and provide timely interventions.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing companies use remote management tools to monitor and control industrial machinery and processes. They can remotely access and configure machines, track production data, and identify potential issues before they lead to disruptions.
- Financial Services: Financial institutions use remote management tools to manage critical infrastructure, such as trading platforms and data centers. These tools ensure the security and availability of sensitive financial data, protecting against cyberattacks and other threats.
Types of Remote Management Tools
Remote management tools empower organizations to control and monitor their IT infrastructure remotely, streamlining operations and improving efficiency. These tools cater to various needs, from accessing and managing individual computers to overseeing entire networks and cloud deployments.
Remote Desktop Software
Remote desktop software enables users to access and control another computer remotely as if they were sitting in front of it. This allows for various tasks, including troubleshooting issues, providing technical support, and accessing files and applications from any location.
- Remote Access: Remote desktop software grants users access to another computer’s desktop, allowing them to view and interact with the screen, keyboard, and mouse.
- File Transfer: Users can transfer files between their local computer and the remote machine, facilitating data sharing and collaboration.
- Remote Control: Users can control the remote computer’s mouse and keyboard, enabling them to execute tasks, navigate applications, and manage settings.
- Remote Assistance: Remote desktop software can be used for remote support, where technicians can assist users with troubleshooting problems or installing software.
Popular examples of remote desktop software include TeamViewer, AnyDesk, and Chrome Remote Desktop.
Network Management Tools
Network management tools are designed to monitor and manage network devices, such as routers, switches, and firewalls. These tools provide real-time insights into network performance, identify potential issues, and facilitate network troubleshooting.
- Network Monitoring: Network management tools collect and analyze network data, such as traffic volume, latency, and device availability, to provide comprehensive network performance insights.
- Device Configuration: These tools enable administrators to configure network devices remotely, including setting up security policies, managing user access, and updating firmware.
- Troubleshooting: Network management tools offer diagnostic capabilities to help identify and resolve network issues, such as performance bottlenecks, connectivity problems, or security breaches.
- Reporting: Network management tools generate reports on network performance, security events, and device usage, providing valuable data for network optimization and planning.
Examples of network management tools include SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, ManageEngine OpManager, and PRTG Network Monitor.
Server Management Tools
Server management tools are specifically designed to manage and monitor servers, including physical servers, virtual machines, and cloud instances. These tools streamline server administration tasks, automate processes, and enhance server performance.
- Server Monitoring: Server management tools monitor server performance metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network activity, to identify potential issues and ensure optimal performance.
- Resource Allocation: These tools enable administrators to allocate resources efficiently, such as CPU cores, memory, and disk space, to optimize server performance and utilization.
- Security Management: Server management tools offer security features, including intrusion detection, vulnerability scanning, and access control, to protect servers from threats.
- Automation: Server management tools automate repetitive tasks, such as software updates, backups, and system patching, reducing administrative overhead and improving efficiency.
Examples of server management tools include VMware vCenter Server, Microsoft System Center, and Red Hat Ansible.
Mobile Device Management (MDM) Tools
Mobile device management (MDM) tools are designed to manage and secure mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, within an organization. These tools allow administrators to control device settings, enforce security policies, and manage applications remotely.
- Device Enrollment: MDM tools allow administrators to enroll devices into the management platform, enabling them to control and monitor these devices.
- Security Policies: MDM tools enable administrators to enforce security policies, such as password requirements, screen lock settings, and data encryption, to protect sensitive information.
- Application Management: MDM tools allow administrators to manage applications on devices, including installing, updating, and removing apps, as well as restricting access to specific apps.
- Data Management: MDM tools can be used to manage device data, such as contacts, calendars, and emails, including backing up data, restoring devices, and wiping data remotely.
Examples of MDM tools include Microsoft Intune, Jamf Pro, and VMware Workspace ONE.
Cloud-Based Management Tools
Cloud-based management tools leverage the power of cloud computing to provide remote management capabilities for various IT resources. These tools offer scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, allowing organizations to manage their IT infrastructure from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Centralized Management: Cloud-based management tools provide a centralized platform for managing multiple IT resources, including servers, applications, and networks, from a single console.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based tools can scale to accommodate growing IT needs, and their flexibility allows organizations to adapt to changing requirements quickly.
- Accessibility: Cloud-based management tools are accessible from any location with an internet connection, enabling administrators to manage their IT infrastructure remotely.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based tools often offer a subscription-based pricing model, which can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premises solutions.
Examples of cloud-based management tools include AWS Management Console, Azure Portal, and Google Cloud Console.
Benefits of Using Remote Management Tools
Remote management tools offer a wide range of advantages that can significantly improve efficiency, security, and overall productivity for businesses of all sizes. By providing the ability to manage and control IT infrastructure from a distance, these tools streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and reduce costs.
Increased Productivity and Efficiency
Remote management tools can boost productivity and efficiency by automating routine tasks and enabling faster troubleshooting.
- Automated tasks: Remote management tools can automate repetitive tasks such as software updates, patch management, and system backups, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Faster troubleshooting: Remote access allows IT professionals to diagnose and resolve issues quickly without needing to physically visit the location. This reduces downtime and minimizes disruptions to business operations.
- Improved resource utilization: By centralizing management, IT teams can optimize resource allocation and ensure efficient use of hardware and software across the organization.
Improved Security and Compliance
Remote management tools play a crucial role in enhancing security and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- Centralized security management: Remote management platforms enable centralized security policies and controls, making it easier to enforce consistent security measures across all devices and systems.
- Real-time monitoring: Remote tools provide real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing IT teams to identify and address potential security threats promptly.
- Improved compliance: Remote management tools help organizations meet compliance requirements by providing audit trails and documentation for security activities.
Reduced Costs and Downtime
Remote management tools can significantly reduce costs and downtime by streamlining operations and minimizing disruptions.
- Reduced travel expenses: Remote access eliminates the need for IT personnel to travel to different locations for troubleshooting or maintenance, saving on travel costs.
- Minimized downtime: Faster troubleshooting and proactive maintenance reduce downtime, minimizing disruptions to business operations and maximizing productivity.
- Optimized resource utilization: Centralized management allows IT teams to optimize resource allocation, reducing the need for additional hardware or software investments.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Remote management tools facilitate collaboration and communication among IT teams, improving efficiency and responsiveness.
- Improved communication: Remote management platforms provide communication channels for IT teams to collaborate and share information effectively.
- Enhanced teamwork: Remote access allows IT professionals to work together seamlessly, regardless of their physical location, enhancing teamwork and knowledge sharing.
- Faster response times: Remote management tools enable IT teams to respond to issues more quickly, improving overall responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
Centralized Control and Management
Remote management tools provide a centralized platform for managing IT infrastructure, simplifying operations and improving control.
- Simplified management: Remote management platforms consolidate IT management tasks, simplifying operations and reducing complexity.
- Improved visibility: Centralized management provides a comprehensive view of the IT infrastructure, enabling IT teams to monitor performance, identify issues, and make informed decisions.
- Enhanced control: Remote management tools provide granular control over devices and systems, allowing IT teams to configure and manage settings remotely.
Key Features of Remote Management Tools
Remote management tools offer a wide range of features that empower IT professionals to effectively manage and control devices and systems remotely. These features streamline operations, enhance security, and optimize resource utilization, enabling organizations to achieve greater efficiency and productivity.
Remote Access and Control
Remote access and control allow IT administrators to connect to and manage remote devices as if they were physically present. This capability is crucial for troubleshooting issues, installing software, configuring settings, and performing other tasks on remote computers, servers, and network devices.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP): RDP is a widely used protocol that enables secure remote desktop access, allowing users to control and interact with a remote computer as if they were sitting in front of it. This is particularly useful for accessing and managing desktops, workstations, and servers located in different locations.
- Secure Shell (SSH): SSH is a secure protocol that allows for secure remote access to servers and network devices. It enables administrators to execute commands, manage files, and monitor system logs, ensuring secure communication and data transfer.
- Virtual Network Computing (VNC): VNC provides a graphical interface for remote access, allowing users to view and control the remote desktop. It is particularly useful for managing devices with graphical user interfaces, such as workstations and servers running graphical applications.
Monitoring and Reporting
Monitoring and reporting functionalities provide real-time insights into the health and performance of remote systems. They allow administrators to track key metrics, identify potential issues, and generate reports for analysis and decision-making.
- System Performance Monitoring: Monitoring tools collect data on system performance, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network traffic. This information helps identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and ensure system stability.
- Security Event Logging: Security monitoring tools track security events, such as login attempts, file access, and network activity. This data is essential for detecting and responding to security threats, ensuring system security and compliance.
- Alerting and Notifications: Monitoring tools can trigger alerts and notifications when predefined thresholds are breached or events occur. This allows administrators to promptly address issues, prevent downtime, and maintain system stability.
- Reporting and Analytics: Remote management tools generate reports and dashboards that provide comprehensive insights into system performance, security events, and other key metrics. These reports facilitate analysis, trend identification, and informed decision-making.
Security and Authentication
Security and authentication are paramount for protecting sensitive data and ensuring secure access to remote systems. Remote management tools incorporate robust security measures to safeguard against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as passwords, one-time codes, or biometrics. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Role-based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC assigns different levels of access to users based on their roles and responsibilities. This ensures that users only have access to the resources they need, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Encryption: Remote management tools use encryption to protect data during transmission and storage. This ensures that data is unreadable to unauthorized parties, safeguarding sensitive information.
- Security Auditing: Auditing functionalities track user activities, system changes, and security events. This data can be used to identify security vulnerabilities, track compliance, and investigate security incidents.
Automation and Scripting
Automation and scripting capabilities streamline repetitive tasks, reduce manual errors, and enhance operational efficiency. Remote management tools allow administrators to automate tasks and implement scripts for routine operations.
- Task Scheduling: Scheduling features enable administrators to automate tasks, such as software updates, backups, and system maintenance, at specific times or intervals. This ensures consistent and reliable execution of critical operations.
- Script Execution: Remote management tools allow administrators to execute scripts remotely, automating complex tasks and reducing manual intervention. This streamlines operations, improves accuracy, and frees up administrators for more strategic tasks.
- Configuration Management: Automation features enable administrators to manage and configure remote systems consistently, ensuring that all devices adhere to predefined standards and policies. This simplifies management, reduces errors, and maintains system stability.
Integration with Other Systems
Remote management tools often integrate with other systems, such as monitoring platforms, ticketing systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) tools. This integration provides a unified view of system health, security events, and operational data, enhancing collaboration and incident response.
- Monitoring Platforms: Integration with monitoring platforms allows administrators to correlate remote system data with other monitoring metrics, providing a holistic view of system performance and potential issues.
- Ticketing Systems: Integration with ticketing systems enables administrators to create and manage support tickets related to remote system issues, streamlining communication and incident resolution.
- SIEM Tools: Integration with SIEM tools allows administrators to centralize security event data from remote systems, enabling comprehensive security analysis, threat detection, and incident response.
Choosing the Right Remote Management Tool
Selecting the perfect remote management tool is crucial for businesses seeking to enhance efficiency, security, and productivity. It involves carefully considering various factors that align with your specific needs and goals.
Budget and Pricing
Budget and pricing play a pivotal role in selecting a remote management tool. It’s essential to analyze your budget constraints and explore tools that fit within your financial limitations.
- Cost-effective options: Consider tools that offer a free tier or a free trial period, allowing you to assess their features and functionality before committing to a paid subscription.
- Subscription models: Evaluate different subscription models, such as monthly, annual, or tiered pricing based on the number of users or devices. Choose a model that aligns with your anticipated usage and budget.
- Hidden costs: Be aware of potential hidden costs, such as additional fees for specific features, support, or integrations. Carefully review the pricing structure and terms of service to avoid unexpected expenses.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are paramount when selecting a remote management tool, as your business grows and your requirements evolve.
- User growth: Choose a tool that can accommodate an increasing number of users without compromising performance or functionality.
- Device management: Ensure the tool can manage a diverse range of devices, including desktops, laptops, smartphones, and tablets, to cater to your evolving IT infrastructure.
- Customization: Look for tools that offer customization options, allowing you to tailor features and settings to your specific needs and workflows.
Compatibility and Integration
Compatibility and integration are critical factors to consider, ensuring seamless integration with your existing IT infrastructure.
- Operating systems: Select a tool compatible with your operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, Linux, or Android. Ensure compatibility with all devices in your environment.
- Existing software: Look for tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing software applications, such as ticketing systems, monitoring tools, or security solutions. This minimizes the need for complex configurations and enhances efficiency.
- API access: Consider tools that offer API access, enabling you to integrate with third-party applications and customize workflows.
User-friendliness and Ease of Use
User-friendliness and ease of use are essential for a smooth and efficient remote management experience.
- Intuitive interface: Opt for a tool with an intuitive and user-friendly interface, minimizing the learning curve and enabling users to quickly navigate and perform tasks.
- Accessibility: Choose a tool accessible across multiple devices and platforms, allowing users to access and manage remote systems from anywhere.
- Training resources: Evaluate the availability of training resources, such as documentation, tutorials, or online support, to assist users in mastering the tool’s features.
Security and Compliance Requirements
Security and compliance are crucial aspects to consider, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- Data encryption: Look for tools that employ strong encryption protocols, protecting data during transmission and storage.
- Two-factor authentication: Choose tools that support two-factor authentication, adding an extra layer of security and preventing unauthorized access.
- Compliance certifications: Ensure the tool meets relevant industry standards and compliance certifications, such as HIPAA, GDPR, or SOC 2, to ensure data security and regulatory adherence.
Implementation and Deployment
Implementing and deploying remote management tools is a crucial step in leveraging their benefits. This involves a systematic approach to ensure smooth integration, efficient configuration, and user-friendly access.
Configuration and Setup
Proper configuration and setup are essential for optimal performance and security.
- Define access policies: Establish clear rules regarding user permissions, access levels, and network restrictions to maintain security and control over managed devices.
- Configure authentication methods: Implement robust authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong passwords, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Set up security protocols: Enable encryption protocols like SSL/TLS to secure data transmission between the remote management tool and managed devices.
- Implement logging and monitoring: Configure logging and monitoring features to track user activities, system events, and potential security threats.
- Integrate with existing systems: Connect the remote management tool with existing IT infrastructure, such as Active Directory or cloud services, for streamlined management.
Training and Support
Training and support are critical to ensure users can effectively utilize remote management tools.
- Provide comprehensive training: Offer hands-on training sessions and documentation to guide users through the features and functionalities of the chosen tool.
- Establish support channels: Provide clear channels for users to seek assistance, such as help desk support, online forums, or dedicated technical teams.
- Develop user guides and FAQs: Create user-friendly guides and frequently asked questions (FAQs) to address common issues and provide quick solutions.
Security Considerations
Remote management tools, while offering significant benefits for managing IT infrastructure, also introduce security risks that need to be carefully addressed. These tools provide access to sensitive data and critical system functions, making them prime targets for malicious actors.
Best Practices for Securing Remote Access and Data
Securing remote access and data is crucial for preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. Implementing robust security measures is essential to protect your systems and data.
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all remote access, requiring users to provide two or more forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code generated by a mobile app. MFA significantly strengthens security by making it much harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implement granular access control policies to restrict user permissions based on their roles and responsibilities. This ensures that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their jobs. For example, a help desk technician should not have access to sensitive financial data.
- Secure Communication Channels: Use encrypted communication protocols like Secure Shell (SSH) and HTTPS to protect data transmitted between remote management tools and managed devices. Encryption ensures that data is unreadable to unauthorized individuals even if intercepted during transmission.
- Regular Security Updates: Regularly update remote management tools and managed devices with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. These updates often include fixes for known security flaws, making it crucial to stay up-to-date.
- Security Monitoring and Logging: Implement security monitoring and logging to detect suspicious activity and potential security breaches. Monitoring tools can track user login attempts, file access, and other relevant events, providing insights into potential threats. Regularly review logs to identify and address any security incidents.
Mitigating Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities, Remote management tools
Mitigating potential risks and vulnerabilities is an ongoing process that involves identifying and addressing security weaknesses in your remote management infrastructure.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Regularly perform vulnerability assessments to identify potential weaknesses in your remote management tools, managed devices, and network infrastructure. These assessments can help uncover security gaps that attackers could exploit.
- Penetration Testing: Conduct penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and identify potential security vulnerabilities. Penetration testing helps assess the effectiveness of your security controls and identify areas for improvement.
- Security Awareness Training: Provide security awareness training to users to educate them about best practices for secure remote access and data handling. Training should cover topics such as strong passwords, phishing scams, and social engineering attacks.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and implement a comprehensive incident response plan to handle security incidents effectively. This plan should Artikel steps for detecting, containing, and recovering from security breaches. Regularly test and update the incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness.
Case Studies and Examples
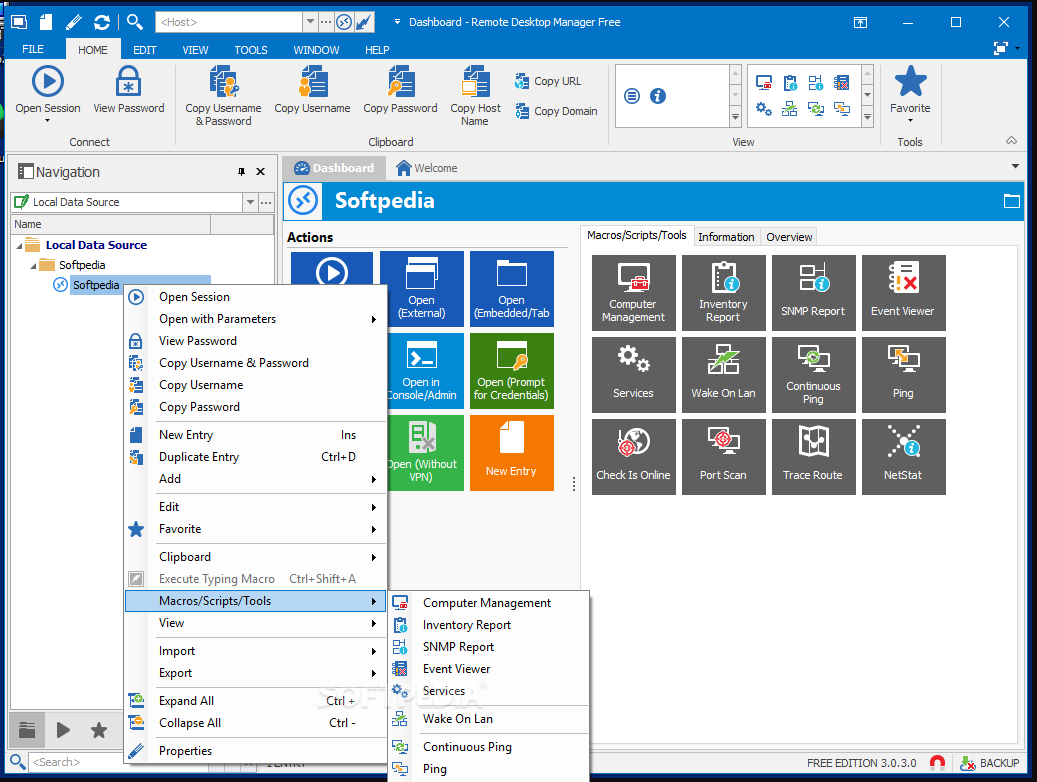
Remote management tools have revolutionized the way organizations manage their IT infrastructure, offering numerous benefits for businesses of all sizes. To illustrate the real-world impact of these tools, let’s delve into some case studies and examples.
Benefits and Challenges in Real-World Implementations
Real-world implementations of remote management tools often involve both benefits and challenges. Let’s explore some examples:
- Case Study: A Large Financial Institution
- Case Study: A Global Retail Chain
- Case Study: A Small Software Development Firm
Benefits of Remote Management Tools in Different Sectors
Remote management tools have proven beneficial across various sectors. Let’s explore some examples:
- Healthcare
- Education
- Manufacturing
- Government
Closing Summary
In conclusion, remote management tools have become an essential component of modern technology, enabling us to navigate the complexities of a digital world with ease and efficiency. By providing remote access, control, and automation, these tools empower us to manage our systems effectively, enhance security, and optimize our productivity, regardless of location. As technology continues to evolve, remote management tools will undoubtedly play an even greater role in shaping the future of how we work, learn, and connect.
Remote management tools are essential for businesses that need to control and monitor their IT infrastructure from afar. One handy tool that can be integrated into remote management is a pdf password remover online which can help securely manage and access sensitive documents, ensuring data integrity and compliance within the organization.