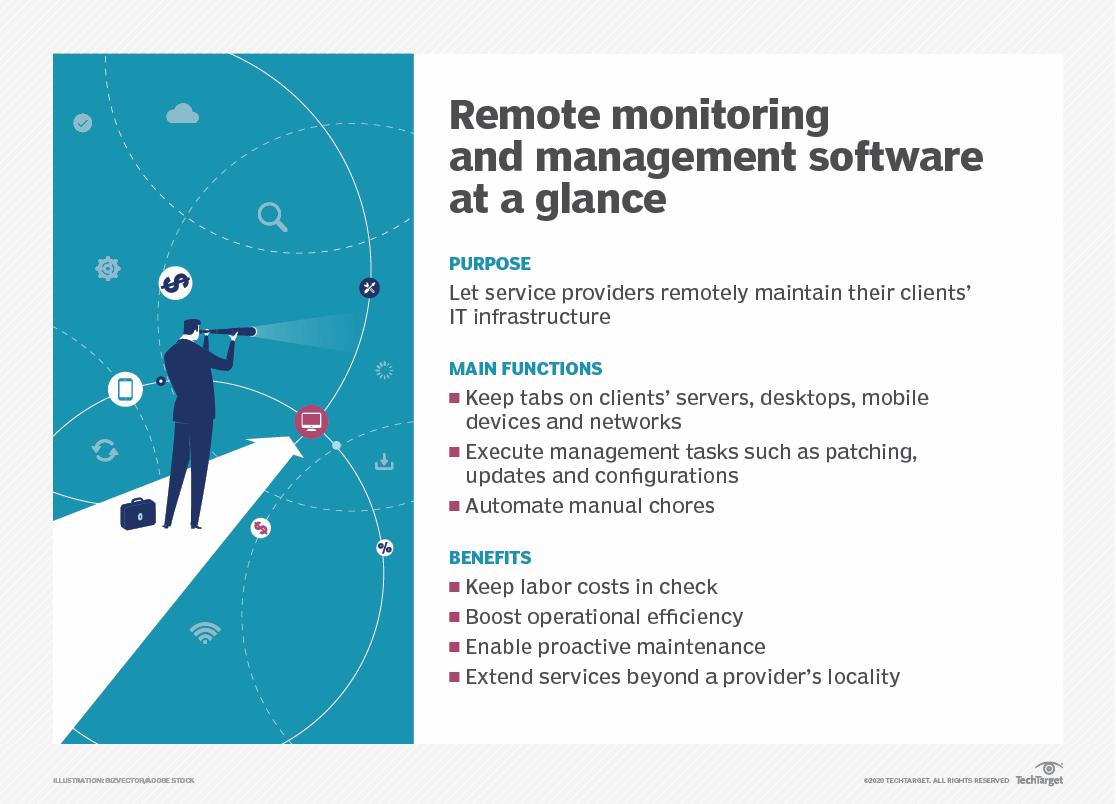
RMM technology sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. RMM, or Remote Monitoring and Management, has revolutionized the way businesses manage their IT infrastructure. Gone are the days of manual, time-consuming tasks; RMM solutions provide a comprehensive suite of tools that automate, monitor, and secure IT operations, empowering IT professionals to focus on strategic initiatives.
Table of Contents
From automating routine tasks like software updates and patch management to providing real-time insights into system performance, RMM solutions have become indispensable for organizations of all sizes. This technology empowers IT teams to proactively address potential issues before they escalate into major problems, ultimately enhancing system stability, security, and overall IT efficiency.
Key Features and Benefits of RMM
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions are essential tools for IT professionals, providing comprehensive oversight and control over their organization’s IT infrastructure. By leveraging advanced features and capabilities, RMM solutions streamline IT operations, enhance security posture, and improve overall efficiency.
Key Features of RMM Solutions
RMM solutions encompass a wide range of features designed to simplify and optimize IT management. Here are some of the most essential features:
- Remote Access and Control: RMM solutions enable IT professionals to access and control remote devices, such as workstations, servers, and mobile devices, securely and efficiently. This capability allows for real-time troubleshooting, software deployment, and system updates, regardless of location.
- Automated Patch Management: Patch management is crucial for maintaining system security and stability. RMM solutions automate the process of identifying, downloading, and installing software updates and security patches across the entire IT infrastructure. This ensures that systems are protected against vulnerabilities and malware.
- Endpoint Security: RMM solutions offer robust endpoint security features, including antivirus protection, malware detection, and intrusion prevention. These capabilities safeguard devices from malicious attacks and data breaches, protecting sensitive information.
- Asset Management: Effective asset management is essential for tracking and managing IT assets, such as hardware, software, and licenses. RMM solutions provide centralized asset inventories, allowing IT professionals to monitor asset utilization, optimize resource allocation, and ensure compliance.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM solutions generate detailed reports and analytics, providing valuable insights into IT performance, security posture, and user behavior. These insights enable IT professionals to identify trends, optimize resource allocation, and make informed decisions.
Benefits of Implementing RMM
Implementing an RMM solution offers numerous advantages for IT teams and organizations. These benefits include:
- Improved Security Posture: RMM solutions enhance security by automating patch management, providing real-time threat monitoring, and implementing endpoint security measures. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of vulnerabilities and data breaches, ensuring the protection of sensitive information.
- Increased Efficiency: RMM solutions automate routine tasks, such as patch management, software deployment, and system updates, freeing up IT professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives. This increased efficiency translates into faster resolution times for IT issues and improved productivity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: RMM solutions help organizations save money by reducing the need for on-site support, minimizing downtime, and optimizing resource allocation. The automation capabilities of RMM solutions streamline IT operations, reducing labor costs and improving overall cost-effectiveness.
- Enhanced User Experience: By proactively managing IT systems and addressing issues before they impact users, RMM solutions contribute to a smoother and more reliable user experience. This translates into increased user satisfaction and improved productivity.
- Improved Compliance: RMM solutions can help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements by automating tasks such as patch management and security audits. This ensures that systems are configured and maintained in accordance with industry standards and regulations.
RMM Deployment and Implementation
Implementing an RMM solution can significantly improve your IT management efficiency and security posture. The process involves careful planning, configuration, and integration with your existing IT infrastructure.
RMM Deployment Process
RMM deployment involves several stages, each crucial for successful implementation.
- Needs Assessment: Determine your specific requirements, including the number of devices to be managed, the types of systems (Windows, macOS, Linux), and the desired level of automation.
- Solution Selection: Choose an RMM solution that aligns with your needs, budget, and technical expertise. Consider factors like features, pricing, scalability, and vendor support.
- Agent Installation: Install the RMM agent on each device you want to manage. This agent gathers data and executes tasks as instructed by the central console.
- Configuration and Integration: Configure the RMM solution according to your preferences, integrating it with existing tools like Active Directory, ticketing systems, and monitoring platforms.
- Testing and Rollout: Thoroughly test the RMM solution in a pilot environment before deploying it to the entire organization. This ensures smooth integration and identifies any potential issues.
- Training and Support: Train your IT team on using the RMM solution effectively and provide ongoing support to ensure smooth operation and address any technical challenges.
Integrating RMM with Existing IT Infrastructure
Seamless integration with your existing IT infrastructure is vital for maximizing the benefits of an RMM solution.
- Active Directory Integration: Integrate the RMM solution with your Active Directory to automate user account management, group policies, and device provisioning.
- Ticketing System Integration: Connect the RMM solution to your ticketing system to automatically create tickets for detected issues, streamline incident resolution, and improve communication between IT staff and users.
- Monitoring Platforms Integration: Integrate the RMM solution with monitoring platforms to provide a centralized view of system performance, security events, and alerts, allowing for proactive issue detection and resolution.
RMM Implementation Best Practices
- Clear Goals and Objectives: Define specific goals and objectives for your RMM implementation, such as improving IT efficiency, enhancing security, or reducing support costs. This helps ensure your RMM investment aligns with your overall IT strategy.
- Pilot Testing: Conduct a pilot test in a controlled environment before deploying the RMM solution to the entire organization. This helps identify potential issues and refine your configuration.
- User Training: Train your IT team and end-users on using the RMM solution effectively. This ensures smooth adoption and maximizes the benefits of the solution.
- Regular Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly monitor the RMM solution’s performance and optimize its configuration to ensure it meets your evolving needs. This includes reviewing logs, monitoring resource usage, and adjusting policies as required.
- Security Best Practices: Implement robust security measures for the RMM solution, including strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates. This helps protect your data and systems from unauthorized access.
RMM Use Cases and Applications
RMM solutions offer a wide range of applications across various industries and organizations, providing significant benefits in managing and securing IT infrastructure. This section explores various use cases and applications of RMM, showcasing its value in diverse scenarios.
RMM Applications in Different Industries, Rmm technology
RMM solutions find applications across various industries, addressing unique IT management challenges.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics rely on RMM to manage critical medical equipment, ensuring patient data security and smooth operations. RMM helps automate routine maintenance tasks, minimize downtime, and enhance patient care.
- Financial Services: Banks and financial institutions leverage RMM for regulatory compliance, data protection, and secure remote access. RMM tools enable centralized control over sensitive financial data, reducing security risks and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Education: Schools and universities utilize RMM to manage student devices, deploy software updates, and troubleshoot technical issues. RMM simplifies IT administration, allowing IT teams to focus on providing better educational support.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing companies rely on RMM for managing industrial control systems, ensuring production uptime, and minimizing downtime. RMM solutions enable remote monitoring and management of critical machinery, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Retail: Retail businesses utilize RMM to manage point-of-sale systems, monitor inventory levels, and ensure smooth customer transactions. RMM helps improve operational efficiency, minimize downtime, and enhance customer experience.
RMM Use Cases Across Different Departments and Roles
RMM solutions cater to various departments and roles within an organization, empowering them to perform their tasks efficiently.
- IT Support: RMM empowers IT support teams to remotely manage and troubleshoot devices, resolving issues quickly and efficiently. Remote access, patch management, and automated tasks streamline support operations, improving service quality.
- Security Teams: RMM plays a crucial role in cybersecurity by automating vulnerability scanning, patching systems, and detecting malicious activity. RMM tools enable proactive security measures, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
- System Administrators: RMM simplifies system administration by automating tasks, monitoring system performance, and managing software updates. This frees up system administrators to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Help Desk: RMM enhances help desk operations by providing remote assistance to users, troubleshooting issues quickly, and resolving problems efficiently. This improves user experience and reduces downtime.
- Executives: RMM provides executives with real-time insights into IT infrastructure performance, security posture, and compliance status. This data enables informed decision-making and strategic planning for IT investments.
Real-World Examples of RMM Solving Business Challenges
RMM solutions have proven their value in addressing real-world business challenges, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and security.
- Healthcare: A large hospital chain implemented RMM to manage its network of medical devices. The solution enabled remote monitoring, automated patching, and proactive maintenance, significantly reducing downtime and improving patient care. The hospital saved millions of dollars in maintenance costs and avoided costly disruptions to critical services.
- Financial Services: A financial institution implemented RMM to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. The solution automated security audits, patch management, and data encryption, ensuring data security and compliance. This reduced the risk of data breaches and fines, safeguarding the institution’s reputation and customer trust.
- Education: A university implemented RMM to manage its student devices. The solution enabled centralized software deployment, remote troubleshooting, and automated updates, streamlining IT administration and reducing support costs. The university improved student satisfaction by providing reliable technical support and ensuring seamless access to learning resources.
Remote Monitoring and Management Tools
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools are essential for IT professionals who need to manage and monitor their clients’ computer systems remotely. These tools offer a wide range of features, including system monitoring, patch management, software deployment, and remote control.
Popular RMM Tools and Platforms
There are many different RMM tools available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here is a comparison of some of the most popular RMM tools:
Key Features, Pricing, and Target Audiences of Different RMM Solutions
| Tool | Key Features | Pricing | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atera | System monitoring, patch management, remote control, ticketing, reporting | Starts at $79 per month | Small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) |
| Datto RMM | System monitoring, patch management, remote control, endpoint security, backup and disaster recovery | Starts at $149 per month | Managed service providers (MSPs) |
| ConnectWise Automate | System monitoring, patch management, remote control, scripting, automation | Starts at $149 per month | MSPs |
| NinjaOne | System monitoring, patch management, remote control, endpoint security, cloud management | Starts at $149 per month | MSPs |
| SolarWinds MSP | System monitoring, patch management, remote control, endpoint security, IT documentation | Starts at $149 per month | MSPs |
Strengths and Weaknesses of Prominent RMM Vendors
| Vendor | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Atera | Easy to use, affordable, good customer support | Limited features compared to some competitors |
| Datto RMM | Comprehensive features, strong security, good integration with other Datto products | Can be expensive, complex to configure |
| ConnectWise Automate | Powerful automation capabilities, extensive scripting language, strong community support | Can be complex to learn, expensive |
| NinjaOne | Cloud-based, scalable, good user interface | Limited reporting features, some features require additional modules |
| SolarWinds MSP | Wide range of features, good reporting capabilities, strong security | Can be complex to configure, expensive |
RMM Security and Compliance
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions are increasingly important for businesses of all sizes. Not only do they improve IT efficiency and productivity, but they also play a crucial role in enhancing security and compliance. By providing a centralized platform for managing and monitoring IT infrastructure, RMM tools help organizations address critical security challenges and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Security Features and Measures
RMM solutions incorporate a range of security features and measures to protect sensitive data and systems. These features can be categorized into several key areas:
- Endpoint Security: RMM tools offer robust endpoint security capabilities, including real-time threat detection, vulnerability scanning, and automated patch management. They can detect and respond to malware, ransomware, and other threats, ensuring that endpoints are protected from malicious attacks.
- Network Security: RMM solutions monitor network activity and identify potential security breaches. They can detect suspicious traffic patterns, unauthorized access attempts, and other network anomalies, helping organizations prevent and mitigate security risks.
- Data Encryption: RMM tools often include data encryption capabilities, ensuring that sensitive information stored on endpoints and in the cloud is protected from unauthorized access. This is particularly important for organizations handling sensitive data, such as financial records, customer information, and intellectual property.
- Access Control: RMM solutions provide granular access control, allowing administrators to restrict access to specific systems and data based on user roles and permissions. This helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): RMM tools can integrate with MFA solutions, adding an extra layer of security to user accounts. This helps prevent unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised.
- Security Auditing: RMM solutions provide comprehensive security auditing capabilities, allowing organizations to track user activity, system changes, and security events. This helps identify potential security breaches and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
RMM and Compliance
RMM solutions play a significant role in helping organizations meet compliance requirements. By automating security tasks and providing a centralized platform for managing and monitoring IT infrastructure, RMM tools can streamline compliance efforts and reduce the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Data Protection Regulations: RMM solutions help organizations comply with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). They provide tools for managing data access, encryption, and deletion, ensuring that organizations can meet the requirements of these regulations.
- Industry-Specific Standards: RMM tools can help organizations comply with industry-specific standards, such as HIPAA for healthcare, PCI DSS for payment card processing, and SOX for financial reporting. They provide features for managing security controls, monitoring compliance activities, and documenting evidence of compliance.
- Security Best Practices: RMM solutions promote the implementation of security best practices, such as regular vulnerability scanning, patch management, and user access control. This helps organizations maintain a secure IT environment and reduce the risk of security breaches.
Potential Security Risks and Mitigation Strategies
While RMM solutions offer significant security benefits, it’s essential to recognize potential security risks associated with their use. Organizations must implement appropriate mitigation strategies to address these risks.
- RMM Tool Vulnerability: RMM tools themselves can be vulnerable to attacks, such as malware infections or unauthorized access. Organizations should ensure that they use reputable RMM solutions with strong security features and regularly update the software to address vulnerabilities.
- Data Breaches: If an RMM tool is compromised, sensitive data stored on endpoints and in the cloud could be exposed. Organizations should implement robust data encryption and access control measures to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Misconfiguration: Incorrect configuration of RMM tools can create security vulnerabilities. Organizations should carefully configure the tools and ensure that they are properly integrated with other security solutions.
- Unauthorized Access: Unauthorized access to RMM tools can lead to security breaches. Organizations should implement strong authentication mechanisms and restrict access to authorized personnel.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate potential security risks associated with RMM tools, organizations should consider the following strategies:
- Use Reputable RMM Solutions: Choose RMM solutions from reputable vendors with a proven track record of security and compliance.
- Regular Software Updates: Regularly update the RMM software to address vulnerabilities and improve security.
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication for all user accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt all sensitive data stored on endpoints and in the cloud.
- Access Control: Implement granular access control to restrict access to specific systems and data based on user roles and permissions.
- Security Auditing: Regularly audit security logs and system configurations to identify potential security vulnerabilities.
- Security Awareness Training: Train employees on security best practices and how to identify and report potential security threats.
RMM Integration with Other Technologies
RMM solutions are designed to streamline IT management, but their power truly shines when integrated with other essential IT tools. These integrations create a cohesive ecosystem, enhancing efficiency, automation, and visibility across your entire IT landscape.
Integration with Ticketing Systems
Integrating RMM with ticketing systems like Zendesk, Jira, or ServiceNow offers several advantages. It allows you to seamlessly link IT issues detected by RMM with support tickets, ensuring prompt resolution. When an RMM agent identifies a problem, it can automatically create a ticket in your chosen ticketing system, complete with relevant details like the affected device, error logs, and system information. This streamlines the troubleshooting process, reducing manual data entry and ensuring consistent information flow.
Integration with Asset Management Tools
RMM integration with asset management tools like Ivanti, ManageEngine, or SolarWinds provides a comprehensive view of your IT assets. By combining data from both systems, you can gain insights into asset utilization, software licenses, and hardware configurations. This information can be used for proactive maintenance, license compliance, and cost optimization.
Integration with Security Solutions
Integrating RMM with security solutions like endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, firewalls, and antivirus software enhances your security posture. This integration enables real-time threat monitoring, automated incident response, and centralized security management. When a security threat is detected, RMM can trigger automated actions, such as quarantining infected devices, applying security patches, or alerting security personnel.
The Future of RMM Technology
The realm of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing demands in the IT landscape. As businesses become increasingly reliant on technology, the need for robust and efficient RMM solutions is paramount. This section explores emerging trends and advancements in RMM, the impact of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the future challenges and opportunities for this critical technology.
Emerging Trends and Advancements in RMM
The RMM landscape is characterized by continuous innovation, with several trends shaping the future of the technology. These trends are driven by factors such as the increasing complexity of IT environments, the growing adoption of cloud computing, and the rise of cyber threats.
- Cloud-Based RMM: The shift towards cloud-based RMM solutions is a major trend. Cloud-based platforms offer several advantages, including scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. They also eliminate the need for on-premises infrastructure, simplifying deployment and management.
- Automation and Orchestration: Automation is becoming increasingly important in RMM. Automated tasks, such as software updates, patch management, and security scans, can significantly improve efficiency and reduce manual effort. Orchestration tools enable the automation of complex workflows, streamlining IT operations.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are transforming various industries, and RMM is no exception. These technologies can be used to analyze data, identify patterns, and predict potential issues, enabling proactive maintenance and security measures. For example, AI-powered tools can monitor system performance, detect anomalies, and predict hardware failures, allowing IT teams to address problems before they impact business operations.
- Integration with Other Technologies: RMM solutions are increasingly integrating with other technologies, such as identity and access management (IAM), security information and event management (SIEM), and ticketing systems. These integrations create a unified IT management platform, enabling seamless workflows and improved collaboration.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning on RMM
AI and ML are playing a transformative role in RMM, enabling more intelligent and proactive management of IT infrastructure. These technologies offer several benefits, including:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze historical data and identify patterns that indicate potential hardware failures. This allows IT teams to proactively schedule maintenance, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
- Enhanced Security: AI-powered security tools can detect and respond to threats in real time. They can analyze network traffic, identify suspicious activity, and automatically implement security measures to prevent breaches. For example, AI can be used to detect and block ransomware attacks before they can encrypt sensitive data.
- Automated Patch Management: AI can be used to automate the patch management process, ensuring that systems are always up-to-date with the latest security updates. This reduces the risk of vulnerabilities and improves overall system security.
- Improved User Experience: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide users with instant support and assistance, resolving common issues and reducing the need for human intervention.
Future Challenges and Opportunities for RMM Technology
While RMM technology is evolving rapidly, it also faces several challenges and opportunities.
- Data Security and Privacy: As RMM solutions collect and analyze large amounts of data, ensuring data security and privacy is paramount. RMM providers must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information and comply with relevant regulations.
- Integration and Interoperability: The integration of RMM solutions with other IT tools is crucial for creating a unified management platform. However, ensuring interoperability between different systems can be challenging. RMM providers need to prioritize open standards and APIs to facilitate seamless integration.
- The Rise of the Edge: As more computing power moves to the edge, RMM solutions will need to adapt to manage devices and applications in distributed environments. This requires a shift towards decentralized management and the development of new tools for monitoring and managing edge devices.
- Skilled Workforce: The adoption of advanced RMM technologies requires a skilled workforce that can manage and maintain these solutions. Training and development programs are essential to ensure that IT professionals have the necessary skills to leverage the full potential of RMM.
RMM and IT Service Management (ITSM)
RMM and ITSM are two critical aspects of IT operations that work together to ensure the smooth functioning and security of an organization’s technology infrastructure. While they have distinct roles, they are deeply intertwined, each complementing and enhancing the other’s capabilities.
ITSM frameworks, such as ITIL, provide a comprehensive approach to managing IT services, encompassing incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management. RMM tools offer real-time monitoring and proactive management of IT assets, enabling organizations to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into service disruptions.
RMM Complements ITSM Processes
RMM solutions seamlessly integrate with ITSM processes, providing valuable insights and automation capabilities. Here’s how RMM complements ITSM:
- Proactive Incident Prevention: RMM tools continuously monitor IT assets, detecting potential issues before they become major incidents. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and reduces the burden on ITSM teams.
- Automated Incident Resolution: RMM can automate the resolution of minor incidents, such as software updates or restarting services, freeing up ITSM teams to focus on more complex issues.
- Enhanced Problem Management: RMM data provides valuable insights into the root causes of incidents, enabling ITSM teams to identify and address recurring problems effectively.
- Improved Change Management: RMM can help manage changes by providing real-time monitoring during deployments, ensuring smooth transitions and minimizing disruptions.
- Real-time Service Level Monitoring: RMM tools provide continuous monitoring of service levels, ensuring compliance with SLAs and enabling ITSM teams to identify and address performance issues promptly.
Best Practices for Integrating RMM with ITSM
Integrating RMM with ITSM frameworks requires a strategic approach to maximize benefits. Here are some best practices:
- Establish Clear Integration Goals: Define the specific objectives for integrating RMM with ITSM, such as improving incident response times, automating routine tasks, or enhancing problem management.
- Select Compatible Tools: Choose RMM and ITSM solutions that offer seamless integration capabilities, ensuring data exchange and process automation.
- Develop a Comprehensive Integration Plan: Create a detailed plan outlining the integration process, including data mapping, workflow adjustments, and user training.
- Implement in Stages: Start with a pilot project to test the integration and refine processes before rolling it out across the organization.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the integration’s effectiveness and make adjustments to optimize performance and address any challenges.
RMM and Cloud Computing
The rise of cloud computing has transformed how businesses operate, with many migrating their IT infrastructure to the cloud. This shift brings new challenges and opportunities for managing IT environments, and RMM plays a crucial role in addressing these needs.
RMM Support for Cloud-Based IT Environments
RMM solutions are designed to monitor and manage IT assets, regardless of their location. This makes them well-suited for managing cloud-based IT environments, which often involve a distributed infrastructure across multiple cloud providers.
- Remote Monitoring and Management: RMM tools enable IT teams to remotely monitor and manage cloud resources, such as servers, applications, and virtual machines. This allows for proactive identification and resolution of issues, minimizing downtime and ensuring service continuity.
- Cloud Security Monitoring: Cloud security is a critical concern, and RMM solutions can help monitor cloud environments for potential threats and vulnerabilities. This includes features like real-time security monitoring, intrusion detection, and compliance reporting.
- Cloud Cost Optimization: Cloud costs can quickly escalate if not managed effectively. RMM solutions can help optimize cloud spending by monitoring resource utilization, identifying idle resources, and recommending cost-saving measures.
- Cloud Asset Management: RMM tools provide comprehensive asset management capabilities, allowing IT teams to track and manage all cloud resources, including servers, databases, applications, and users. This helps ensure compliance, optimize resource allocation, and facilitate cloud migration projects.
Challenges and Opportunities of Managing Cloud Infrastructure with RMM
While RMM offers significant benefits for managing cloud environments, there are also challenges to consider.
- Integration with Cloud Providers: Integrating RMM solutions with different cloud providers can be complex, requiring careful planning and configuration. Each cloud provider has its own APIs and protocols, which RMM tools need to support.
- Data Security and Compliance: Managing sensitive data in the cloud requires robust security measures, and RMM tools need to comply with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA.
- Scalability and Performance: Cloud environments can scale rapidly, requiring RMM solutions to handle increased workloads and maintain performance. This is especially important for large-scale cloud deployments.
- Cost Considerations: RMM solutions for cloud environments can come with additional costs, such as subscription fees and integration services. It’s important to carefully evaluate the cost-benefit analysis before adopting an RMM solution.
Examples of RMM Solutions for Cloud Environments
Several RMM solutions are specifically designed for managing cloud environments.
- Datto RMM: Datto RMM offers comprehensive cloud management capabilities, including monitoring, patching, and security for various cloud providers, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- ConnectWise Automate: ConnectWise Automate provides a robust cloud management platform, allowing IT teams to manage cloud resources, automate tasks, and monitor security threats.
- NinjaOne: NinjaOne offers a cloud-based RMM solution that supports various cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, and VMware. It provides comprehensive monitoring, management, and security features.
RMM and Automation: Rmm Technology
RMM solutions are designed to streamline and simplify IT management tasks, and automation plays a pivotal role in achieving this goal. By automating repetitive and time-consuming processes, RMM empowers IT professionals to focus on strategic initiatives and enhance overall efficiency.
Automation of IT Tasks
RMM facilitates automation of various IT tasks, significantly reducing manual effort and potential for errors.
- Patch Management: RMM tools automate the process of identifying, downloading, and installing software updates for operating systems and applications. This ensures systems are protected from vulnerabilities and remain up-to-date.
- Software Deployment: RMM enables the automated deployment of software applications to multiple devices, ensuring consistent configurations and reducing the need for manual installation on each machine.
- Backup and Recovery: RMM solutions can automate data backups, scheduling regular backups and ensuring data integrity. In case of system failures, automated recovery procedures can restore data and minimize downtime.
- System Monitoring: RMM tools can monitor system performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space, and trigger alerts when predefined thresholds are exceeded. This enables proactive identification and resolution of potential issues before they impact users.
- Security Policies: RMM platforms allow for the automation of security policy enforcement, ensuring consistent security measures across all managed devices. This includes tasks like password complexity enforcement, firewall configuration, and anti-malware updates.
- User Management: RMM solutions can automate user account creation, modification, and deletion, simplifying user management tasks and maintaining security. This includes tasks like password resets, account provisioning, and access control.
- Hardware Inventory: RMM tools can automatically collect hardware inventory data, providing a comprehensive overview of devices and their configurations. This information is crucial for asset management, capacity planning, and troubleshooting.
Benefits of Automation in IT Management
Automation offers numerous benefits for IT management, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and overall IT service delivery.
- Increased Efficiency: Automation eliminates repetitive tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic and complex initiatives. This results in a significant increase in overall efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced Errors: Manual tasks are prone to errors, but automation ensures consistency and accuracy. By eliminating human intervention in repetitive processes, RMM reduces the risk of errors and improves data integrity.
- Improved Compliance: Automation helps ensure compliance with industry regulations and best practices. RMM tools can automatically enforce security policies, patch vulnerabilities, and perform regular backups, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
- Enhanced Security: Automation strengthens security by automating tasks like vulnerability patching, firewall configuration, and malware detection. This proactive approach helps prevent security breaches and protect sensitive data.
- Cost Savings: Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, resulting in cost savings through reduced labor requirements and improved efficiency. This allows IT departments to optimize resource allocation and focus on value-adding activities.
- Improved Service Delivery: Automation enables faster resolution of IT issues, leading to improved service delivery and increased user satisfaction. By automating routine tasks, IT teams can respond to user requests and resolve problems more efficiently.
Final Conclusion
As we delve deeper into the world of RMM technology, we uncover its transformative potential for modern IT management. From simplifying complex tasks to bolstering security and compliance, RMM empowers businesses to streamline their operations, optimize resource allocation, and achieve their strategic goals. The future of RMM holds even more promise, with the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning poised to further enhance its capabilities. Embracing RMM technology is not just a strategic decision, but a necessary step towards building a resilient, secure, and efficient IT infrastructure for the future.
RMM technology streamlines IT management, ensuring smooth operation of your systems. A key aspect of this is managing software updates, which often involves downloading the latest versions. For a reliable source of software downloads, check out App Genius Lab.
Once you’ve got the software, RMM tools can help you automate deployment and ensure consistent updates across your network.
